Dose-dependent modulation of CD8 and functional avidity as a result of peptide encounter
- PMID: 17484768
- PMCID: PMC2266002
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02622.x
Dose-dependent modulation of CD8 and functional avidity as a result of peptide encounter
Abstract
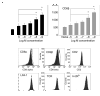
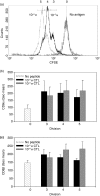
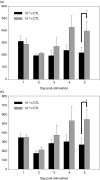
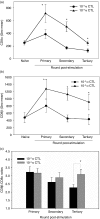
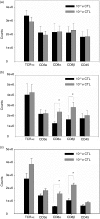
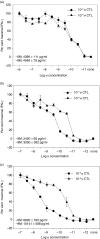
The generation of an optimal CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) response is critical for the clearance of many intracellular pathogens. Previous studies suggest that one contributor to an optimal immune response is the presence of CD8(+) cells exhibiting high functional avidity. In this regard, CD8 expression has been shown to contribute to peptide sensitivity. Here, we investigated the ability of naive splenocytes to modulate CD8 expression according to the concentration of stimulatory peptide antigen. Our results showed that the level of CD8 expressed was inversely correlated with the amount of peptide used for the primary stimulation, with higher concentrations of antigen resulting in lower expression of both CD8alpha and CD8beta. Importantly the ensuing CD8(low) and CD8(high) CTL populations were not the result of the selective outgrowth of naive CD8(+) T-cell subpopulations expressing distinct levels of CD8. Subsequent encounter with peptide antigen resulted in continued modulation of both the absolute level and the isoform of CD8 expressed and in the functional avidity of the responding cells. We propose that CD8 cell surface expression is not a static property, but can be modulated to 'fine tune' the sensitivity of responding CTL to a defined concentration of antigen.
Figures

References
-
- Yee C, Savage PA, Lee PP, et al. Isolation of high avidity melanoma-reactive CTL from heterogeneous populations using peptide-MHC tetramers. J Immunol. 1999;162:2227–34. - PubMed
-
- Zeh HJ, III, Perry-Lalley D, Dudley ME, et al. High avidity CTLs for two self-antigens demonstrate superior in vitro and in vivo antitumor efficacy. J Immunol. 1999;162:989–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

