Expression of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) in T lymphocytes
- PMID: 17484769
- PMCID: PMC2265994
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02621.x
Expression of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) in T lymphocytes
Abstract
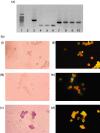
5-Lipoxygenase (5-LOX) is the key enzyme responsible for the synthesis of the biologically active leukotrienes. Its presence has been reported in cells of the myeloid lineage and B lymphocytes but has not been formally defined in T lymphocytes. In this study, we provide evidence for 5-LOX expression on both transcriptional and translational levels in highly purified peripheral blood T cells as well as in human T lymphoblastoid cell lines (MOLT4 and Jurkat). Messenger RNA (mRNA) of 5-LOX was amplified by conventional reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR; MOLT4 and Jurkat cells) and by in situ RT-PCR (T lymphocytes). 5-LOX protein expression was confirmed by Western blot and immunofluorescence studies. 5-LOX was present primarily in the cytoplasm with some nuclear localization and was translocated to the nuclear periphery after culture in a mitosis-supporting medium. Fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis of different T-lymphocyte populations, including CD4, CD8, CD45RO, CD45RA, T helper type 2, and T-cell receptor-alphabeta and -gammadelta expressing cells, did not identify a differential distribution of the enzyme. Purified peripheral blood T lymphocytes were incapable of synthesizing leukotrienes in the absence of exogenous arachidonic acid. Jurkat cells produced leukotriene C(4) and a small amount of leukotriene B(4) in response to CD3-CD28 cross-linking. This synthesis was abolished by two inhibitors of leukotriene synthesis, MK-886 and AA-861. The presence of 5-LOX in T lymphocytes but the absence of endogenous lipoxygenase metabolite production compared to Jurkat cells may constitute a fundamental difference between resting peripheral lymphocytes and leukaemic cells.
Figures



References
-
- Funk CD. Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: advances in eicosanoid biology. Science. 2001;294:1871–5. - PubMed
-
- Ruegg C, Dormond O, Mariotti A. Endothelial cell integrins and COX-2: mediators and therapeutic targets of tumor angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1654:51–67. - PubMed
-
- Goodwin JS, Ceuppens J. Regulation of the immune response by prostaglandins. J Clin Immunol. 1983;3:295–315. - PubMed
-
- Stjernschantz J. The leukotrienes. Med Biol. 1984;62:215–30. - PubMed
-
- Rouzer CA, Kargman S. Translocation of 5-lipoxygenase to the membrane in human leukocytes challenged with ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:10980–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

