Study of active controlled monotherapy used for rheumatoid arthritis, an IL-6 inhibitor (SAMURAI): evidence of clinical and radiographic benefit from an x ray reader-blinded randomised controlled trial of tocilizumab
- PMID: 17485422
- PMCID: PMC1955155
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.068064
Study of active controlled monotherapy used for rheumatoid arthritis, an IL-6 inhibitor (SAMURAI): evidence of clinical and radiographic benefit from an x ray reader-blinded randomised controlled trial of tocilizumab
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the ability of tocilizumab (a humanised anti-IL-6 receptor antibody) monotherapy to inhibit progression of structural joint damage in patients with RA.
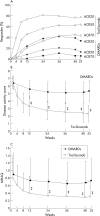
Methods: In a multi-centre, x ray reader-blinded, randomised, controlled trial, 306 patients with active RA of <5 years' duration were allocated to receive either tocilizumab monotherapy at 8 mg/kg intravenously every 4 weeks or conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for 52 weeks. Radiographs of hands and forefeet were scored by the van der Heijde modified Sharp method.
Results: Patients had a mean disease duration of 2.3 years and a disease activity score in 28 joints of 6.5 at baseline. Mean total modified Sharp score (TSS) was 29.4, which was very high despite the relatively short disease duration. At week 52, the tocilizumab group showed statistically significantly less radiographic change in TSS (mean 2.3; 95% CI 1.5 to 3.2) than the DMARD group (mean 6.1; 95% CI 4.2 to 8.0; p<0.01). Tocilizumab monotherapy also improved signs and symptoms. The overall incidences of AEs were 89% and 82% (serious AEs: 18% and 13%; serious infections: 7.6% and 4.1%) in the tocilizumab and DMARD groups, respectively.
Conclusion: Tocilizumab monotherapy was generally well tolerated and provided radiographic benefit in patients with RA.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: NN has served as a consultant to and/or received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical, the manufacture of tocilizumab. TK holds a patent for tocilizumab. The other authors have no competing interests.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical