Hematopoiesis and thymic apoptosis are not affected by the loss of Cdk2
- PMID: 17485443
- PMCID: PMC1951952
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00029-07
Hematopoiesis and thymic apoptosis are not affected by the loss of Cdk2
Abstract
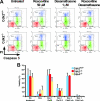
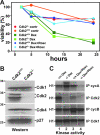
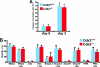
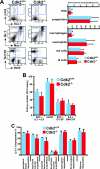
Cell cycle regulation is essential for proper homeostasis of hematopoietic cells. Cdk2 is a major regulator of S phase entry, is activated by mitogenic cytokines, and has been suggested to be involved in antigen-induced apoptosis of T lymphocytes. The role of Cdk2 in hematopoietic cells and apoptosis in vivo has not yet been addressed. To determine whether Cdk2 plays a role in these cells, we performed multiple analyses of bone marrow cells, thymocytes, and splenocytes from Cdk2 knockout mice. We found that Cdk2 is not required in vivo to induce apoptosis in lymphocytes, a result that differs from previous pharmacological in vitro studies. Furthermore, thymocyte maturation was not affected by the lack of Cdk2. We then analyzed the hematopoietic stem cell compartment and found similar proportions of stem cells and progenitors in Cdk2(-)(/)(-) and wild-type animals. Knockouts of Cdk2 inhibitors (p21, p27) affect stem cell renewal, but a competitive graft experiment indicated that renewal and multilineage differentiation are normal in the absence of Cdk2. Finally, we stimulated T lymphocytes or macrophages to induce proliferation and observed normal reactivation of Cdk2(-)(/)(-) quiescent cells. Our results indicate that Cdk2 is not required for proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic cells in vivo, although in vitro analyses consider Cdk2 to be a major player in proliferation and apoptosis in these cells and a potential target for therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Aleem, E., and P. Kaldis. 2006. Mouse models of cell cycle regulators: new paradigms. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 42:271-328. - PubMed
-
- Aleem, E., H. Kiyokawa, and P. Kaldis. 2005. Cdc2-cyclin E complexes regulate the G1/S phase transition. Nat. Cell Biol. 7:831-836. - PubMed
-
- Bergh, G., M. Ehinger, I. Olsson, S. E. Jacobsen, and U. Gullberg. 1999. Involvement of the retinoblastoma protein in monocytic and neutrophilic lineage commitment of human bone marrow progenitor cells. Blood 94:1971-1978. - PubMed
-
- Berthet, C., E. Aleem, V. Coppola, L. Tessarollo, and P. Kaldis. 2003. Cdk2 knockout mice are viable. Curr. Biol. 13:1775-1785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
