Pathogen-induced binding of the soybean zinc finger homeodomain proteins GmZF-HD1 and GmZF-HD2 to two repeats of ATTA homeodomain binding site in the calmodulin isoform 4 (GmCaM4) promoter
- PMID: 17485478
- PMCID: PMC1920248
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm273
Pathogen-induced binding of the soybean zinc finger homeodomain proteins GmZF-HD1 and GmZF-HD2 to two repeats of ATTA homeodomain binding site in the calmodulin isoform 4 (GmCaM4) promoter
Abstract
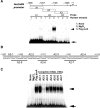
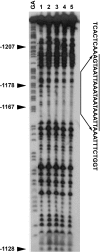
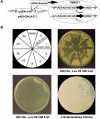
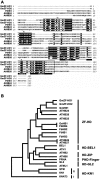
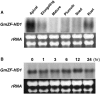
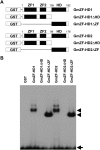
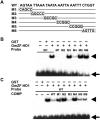
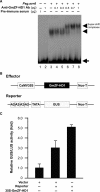
Calmodulin (CaM) is involved in defense responses in plants. In soybean (Glycine max), transcription of calmodulin isoform 4 (GmCaM4) is rapidly induced within 30 min after pathogen stimulation, but regulation of the GmCaM4 gene in response to pathogen is poorly understood. Here, we used the yeast one-hybrid system to isolate two cDNA clones encoding proteins that bind to a 30-nt A/T-rich sequence in the GmCaM4 promoter, a region that contains two repeats of a conserved homeodomain binding site, ATTA. The two proteins, GmZF-HD1 and GmZF-HD2, belong to the zinc finger homeodomain (ZF-HD) transcription factor family. Domain deletion analysis showed that a homeodomain motif can bind to the 30-nt GmCaM4 promoter sequence, whereas the two zinc finger domains cannot. Critically, the formation of super-shifted complexes by an anti-GmZF-HD1 antibody incubated with nuclear extracts from pathogen-treated cells suggests that the interaction between GmZF-HD1 and two homeodomain binding site repeats is regulated by pathogen stimulation. Finally, a transient expression assay with Arabidopsis protoplasts confirmed that GmZF-HD1 can activate the expression of GmCaM4 by specifically interacting with the two repeats. These results suggest that the GmZF-HD1 and -2 proteins function as ZF-HD transcription factors to activate GmCaM4 gene expression in response to pathogen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Specificity of DNA sequences recognized by the zinc-finger homeodomain protein, GmZF-HD1 in soybean.Phytochemistry. 2010 Nov;71(16):1832-8. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.07.010. Phytochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20804996
-
The members of zinc finger-homeodomain (ZF-HD) transcription factors are associated with abiotic stresses in soybean: insights from genomics and expression analysis.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jan 14;25(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-06028-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39810081 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the stress-inducible soybean calmodulin isoform-4 (GmCaM-4) promoter in transgenic tobacco plants.Mol Cells. 2009 Apr 30;27(4):475-80. doi: 10.1007/s10059-009-0063-6. Epub 2009 Apr 13. Mol Cells. 2009. PMID: 19390829
-
Characterization of a novel class of plant homeodomain proteins that bind to the C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene of Flaveria trinervia.Plant Mol Biol. 2001 Jan;45(2):201-14. doi: 10.1023/a:1006450005648. Plant Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11289511
-
Zinc Finger-Homeodomain and Mini Zinc Finger proteins are key players in plant growth and responses to environmental stresses.J Exp Bot. 2022 Aug 11;73(14):4662-4673. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac194. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 35536651 Review.
Cited by
-
Stress induced and nuclear localized HIPP26 from Arabidopsis thaliana interacts via its heavy metal associated domain with the drought stress related zinc finger transcription factor ATHB29.Plant Mol Biol. 2009 Jan;69(1-2):213-26. doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9419-0. Epub 2008 Oct 31. Plant Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 18974936
-
Battle through signaling between wheat and the fungal pathogen Septoria tritici revealed by proteomics and phosphoproteomics.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Sep;12(9):2497-508. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.027532. Epub 2013 May 29. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23722186 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Finger-Homeodomain Genes: Evolution, Functional Differentiation, and Expression Profiling Under Flowering-Related Treatments and Abiotic Stresses in Plants.Evol Bioinform Online. 2019 Sep 5;15:1176934319867930. doi: 10.1177/1176934319867930. eCollection 2019. Evol Bioinform Online. 2019. PMID: 31523124 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the Role of Promoters of Pathogen-sensitive Genes in Plant Defense.Curr Genomics. 2020 Nov;21(7):491-503. doi: 10.2174/1389202921999200727213500. Curr Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33214765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZF-HD gene family in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): genome-wide identification, phylogeny, evolutionary expansion and expression analyses.BMC Genomics. 2024 Dec 5;25(1):1181. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11102-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39639240 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gilroy S, Bethke PC, Jones RL. Calcium homeostasis in plants. J. Cell Sci. 1993;106:453–461. - PubMed
-
- Knight MR, Campbell AK, Smith SM, Trewavas AJ. Transgenic plant aequorin reports the effects of touch and cold-shock and elicitors on cytoplasmic calcium. Nature. 1991;352:524–526. - PubMed
-
- Dixon RA, Harrison MJ, Lamb CJ. Early events in the activation of plant defense responses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1994;32:479–501.
-
- Dolmetsch RE, Lewis RS, Goodnow CC, Healy JI. Differential activation of transcription factors induced by Ca2+ response amplitude and duration. Nature. 1997;24:855–858. - PubMed
-
- Sacks WR, Ferreira P, Hahlbrock K, Jabs T, Nürnberger T, Renelt A, Scheel D. In: Advances in Molecular Genetics of Plant-Microbe Interactions. Nester EW, Verma DPS, editors. Vol. 2. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer; 1993. pp. 485–495.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

