Emi1 is needed to couple DNA replication with mitosis but does not regulate activation of the mitotic APC/C
- PMID: 17485488
- PMCID: PMC2064829
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200611166
Emi1 is needed to couple DNA replication with mitosis but does not regulate activation of the mitotic APC/C
Abstract
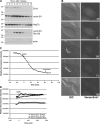
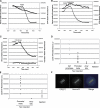
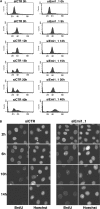
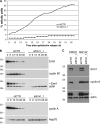
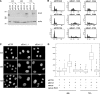
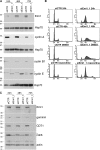
Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis is critical for the alternation between DNA replication and mitosis and for the key regulatory events in mitosis. The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is a conserved ubiquitin ligase that has a fundamental role in regulating mitosis and the cell cycle in all eukaryotes. In vertebrate cells, early mitotic inhibitor 1 (Emi1) has been proposed as an important APC/C inhibitor whose destruction may trigger activation of the APC/C at mitosis. However, in this study, we show that the degradation of Emi1 is not required to activate the APC/C in mitosis. Instead, we uncover a key role for Emi1 in inhibiting the APC/C in interphase to stabilize the mitotic cyclins and geminin to promote mitosis and prevent rereplication. Thus, Emi1 plays a crucial role in the cell cycle to couple DNA replication with mitosis, and our results also question the current view that the APC/C has to be inactivated to allow DNA replication.
Figures

References
-
- Amon, A., S. Irniger, and K. Nasmyth. 1994. Closing the cell cycle circle in yeast: G2 cyclin proteolysis initiated at mitosis persists until the activation of G1 cyclins in the next cycle. Cell. 77:1037–1050. - PubMed
-
- Broek, D., R. Bartlett, K. Crawford, and P. Nurse. 1991. Involvement of p34cdc2 in establishing the dependency of S phase on mitosis. Nature. 349:388–393. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp, T.R., R. Bernards, and R. Agami. 2002. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 296:550–553. - PubMed
-
- Castro, A., C. Bernis, S. Vigneron, J.C. Labbe, and T. Lorca. 2005. The anaphase-promoting complex: a key factor in the regulation of cell cycle. Oncogene. 24:314–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

