p400 function is required for the adenovirus E1A-mediated suppression of EGFR and tumour cell killing
- PMID: 17486071
- PMCID: PMC4591001
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210497
p400 function is required for the adenovirus E1A-mediated suppression of EGFR and tumour cell killing
Abstract
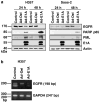
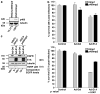
We have recently shown that E1A protein of human adenovirus downregulates epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression and induces apoptosis in head and neck (HNSCC) and lung cancer cells independently of their p53 status. E1A has five isoforms of which the major ones E1A12S and E1A13S regulate transcription of cellular genes by binding to transcriptional modulators such as pRB, CtBP, p300 and p400. In this study, we have identified E1A12S isoform to have the highest effect on EGFR suppression and induction of apoptosis in HNSCC cells. Similar to Ad5, E1A12S from human adenovirus types 2, 3, 9 and 12 suppressed EGFR, whereas E1A12S of adenovirus types 4 and 40 had no effect on EGFR expression. Using deletion mutants of E1A12S we have shown that interaction of E1A with p400, but not p300 or pRB, is required for EGFR suppression and apoptosis. Inhibition of p400 by short hairpin RNA confirmed that HNSCC cells with reduced p400 expression were less sensitive to E1A-induced suppression of EGFR and apoptosis. p300 function was shown to be dispensable, as cells expressing E1A mutants that are unable to bind p300, or p300 knockout cells, remained sensitive to E1A-induced apoptosis. In summary, this study identifies p400 as an important mediator of E1A-induced downregulation of EGFR and apoptosis.
Figures





References
-
- Avvakumov N, Kajon AE, Hoeben RC, Mymryk JS. Comprehensive sequence analysis of the E1A proteins of human and simian adenoviruses. Virology. 2004;329:477–492. - PubMed
-
- Barbeau D, Charbonneau R, Whalen SG, Bayley ST, Branton PE. Functional interactions within adenovirus E1A protein complexes. Oncogene. 1994;9:359–373. - PubMed
-
- Bergman LM, Blaydes JP. C-terminal binding proteins: emerging roles in cell survival and tumorigenesis. Apoptosis. 2006;11:879–888. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

