Generation of functional hemangioblasts from human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 17486087
- PMCID: PMC3766360
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth1041
Generation of functional hemangioblasts from human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Recent evidence suggests the existence of progenitor cells in adult tissues that are capable of differentiating into vascular structures as well as into all hematopoietic cell lineages. Here we describe an efficient and reproducible method for generating large numbers of these bipotential progenitors-known as hemangioblasts-from human embryonic stem (hES) cells using an in vitro differentiation system. Blast cells expressed gene signatures characteristic of hemangioblasts, and could be expanded, cryopreserved and differentiated into multiple hematopoietic lineages as well as into endothelial cells. When we injected these cells into rats with diabetes or into mice with ischemia-reperfusion injury of the retina, they localized to the site of injury in the damaged vasculature and appeared to participate in repair. Injection of the cells also reduced the mortality rate after myocardial infarction and restored blood flow in hind limb ischemia in mouse models. Our data suggest that hES-derived blast cells (hES-BCs) could be important in vascular repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: details accompany the full-text HTML version of the paper at
Figures
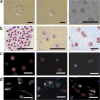

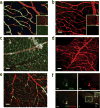
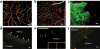

References
-
- Rafii S, Lyden D. Therapeutic stem and progenitor cell transplantation for organ vascularization and regeneration. Nat Med. 2003;9:702–712. - PubMed
-
- Grant MB, et al. Adult hematopoietic stem cells provide functional hemangioblast activity during retinal neovascularization. Nat Med. 2002;8:607–612. - PubMed
-
- Bailey AS, et al. Transplanted adult hematopoietic stems cells differentiate into functional endothelial cells. Blood. 2004;103:13–19. - PubMed
-
- Cogle CR, et al. Adult human hematopoietic cells provide functional hemangioblast activity. Blood. 2004;103:133–135. - PubMed
-
- Otani A, et al. Bone marrow-derived stem cells target retinal astrocytes and can promote or inhibit retinal angiogenesis. Nat Med. 2002;8:1004–1010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

