Positional stability of single double-strand breaks in mammalian cells
- PMID: 17486118
- PMCID: PMC2442898
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1591
Positional stability of single double-strand breaks in mammalian cells
Abstract
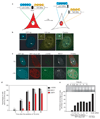
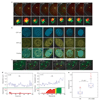
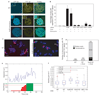
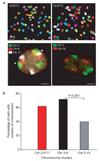
Formation of cancerous translocations requires the illegitimate joining of chromosomes containing double-strand breaks (DSBs). It is unknown how broken chromosome ends find their translocation partners within the cell nucleus. Here, we have visualized and quantitatively analysed the dynamics of single DSBs in living mammalian cells. We demonstrate that broken ends are positionally stable and unable to roam the cell nucleus. Immobilization of broken chromosome ends requires the DNA-end binding protein Ku80, but is independent of DNA repair factors, H2AX, the MRN complex and the cohesion complex. DSBs preferentially undergo translocations with neighbouring chromosomes and loss of local positional constraint correlates with elevated genomic instability. These results support a contact-first model in which chromosome translocations predominantly form among spatially proximal DSBs.
Figures
References
-
- Kanaar R, Hoeijmakers JH, van Gent DC. Molecular mechanisms of DNA double strand break repair. Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8:483–489. - PubMed
-
- Khanna KK, Jackson SP. DNA double-strand breaks: signaling, repair and the cancer connection. Nature Genet. 2001;27:247–254. - PubMed
-
- Nikiforova MN, et al. Proximity of chromosomal loci that participate in radiation-induced rearrangements in human cells. Science. 2000;290:138–141. - PubMed

