Three-dimensional confocal morphometry - a new approach for studying dynamic changes in cell morphology in brain slices
- PMID: 17488344
- PMCID: PMC2375758
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00724.x
Three-dimensional confocal morphometry - a new approach for studying dynamic changes in cell morphology in brain slices
Abstract
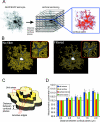
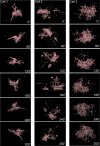
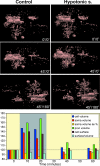
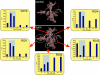
Pathological states in the central nervous system lead to dramatic changes in the activity of neuroactive substances in the extracellular space, to changes in ionic homeostasis and often to cell swelling. To quantify changes in cell morphology over a certain period of time, we employed a new technique, three-dimensional confocal morphometry. In our experiments, performed on enhanced green fluorescent protein/glial fibrillary acidic protein astrocytes in brain slices in situ and thus preserving the extracellular microenvironment, confocal morphometry revealed that the application of hypotonic solution evoked two types of volume change. In one population of astrocytes, hypotonic stress evoked small cell volume changes followed by a regulatory volume decrease, while in the second population volume changes were significantly larger without subsequent volume regulation. Three-dimensional cell reconstruction revealed that even though the total astrocyte volume increased during hypotonic stress, the morphological changes in various cell compartments and processes were more complex than have been previously shown, including swelling, shrinking and structural rearrangement. Our data show that astrocytes in brain slices in situ during hypotonic stress display complex behaviour. One population of astrocytes is highly capable of cell volume regulation, while the second population is characterized by prominent cell swelling, accompanied by plastic changes in morphology. It is possible to speculate that these two astrocyte populations play different roles during physiological and pathological states.
Figures
References
-
- Aitken PG, Borgdorff AJ, Juta AJ, Kiehart DP, Somjen GG, Wadman WJ. Volume changes induced by osmotic stress in freshly isolated rat hippocampal neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1998;436:991–998. - PubMed
-
- Allansson L, Khatibi S, Gustavsson T, Blomstrand F, Olsson T, Hansson E. Single-cell volume estimation by three-dimensional wide-field microscopy applied to astroglial primary cultures. J Neurosci Meth. 1999;93:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Anděrová M, Antonova T, Petřík D, Neprašová H, Chvátal A, Syková E. Voltage-dependent potassium currents in hypertrophied rat astrocytes after a cortical stab wound. Glia. 2004;48:311–326. - PubMed
-
- Andrew RD, Lobinowich ME, Osehobo EP. Evidence against volume regulation by cortical brain cells during acute osmotic stress. Exp Neurol. 1997;143:300–312. - PubMed
-
- Ballanyi K, Grafe P, Serve G, Schlue WR. Electrophysiological measurements of volume changes in leech neuropile glial cells. Glia. 1990;3:151–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

