Effective therapy of murine models of human leukemia and lymphoma with radiolabeled anti-CD30 antibody, HeFi-1
- PMID: 17488826
- PMCID: PMC1895969
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0702496104
Effective therapy of murine models of human leukemia and lymphoma with radiolabeled anti-CD30 antibody, HeFi-1
Abstract
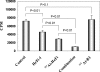
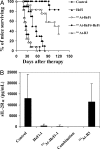
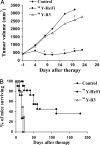
CD30 is a member of the TNF receptor superfamily. Overexpression of CD30 on some neoplasms versus limited expression on normal tissues makes this receptor a promising target for antibody-based therapy. Radioimmunotherapy of cancer with radiolabeled antibodies has shown promise. In this study, we evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of an anti-CD30 antibody, HeFi-1, armed with (211)At in a leukemia (karpas299) model and with (90)Y in a lymphoma (SUDHL-1) model. Furthermore, we investigated the combination therapy of (211)At-HeFi-1 with unmodified HeFi-1 in the leukemia model. Treatment with unmodified HeFi-1 significantly prolonged the survival of the karpas299-bearing mice compared with the controls (P < 0.001). Treatment with (211)At-HeFi-1 showed greater therapeutic efficacy than that with unmodified HeFi-1 as shown by survival of the mice (P < 0.001). Combining these two agents further improved the survival of the mice compared with the groups treated with either (211)At-HeFi-1 (P < 0.05) or unmodified HeFi-1 (P < 0.001) alone. In the lymphoma model, the survival of the SUDHL-1-bearing mice was significantly prolonged by the treatment with (90)Y-HeFi-1 compared with the controls (P < 0.001). In summary, radiolabeled HeFi-1 is very promising for the treatment of CD30-expressing leukemias and lymphomas, and the combination regimen of (211)At-HeFi-1 with unmodified HeFi-1 enhanced the therapeutic efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
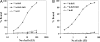
Similar articles
-
Effective therapy for a murine model of human anaplastic large-cell lymphoma with the anti-CD30 monoclonal antibody, HeFi-1, does not require activating Fc receptors.Blood. 2006 Jul 15;108(2):705-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-11-4607. Epub 2006 Mar 21. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16551968 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-CD25 monoclonal antibody 7G7/B6, armed with the alpha-emitter 211At, provides effective radioimmunotherapy for a murine model of leukemia.Cancer Res. 2006 Aug 15;66(16):8227-32. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1189. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16912202
-
Preclinical evaluation of 64Cu/177Lu-labelled anti-CD30 monoclonal antibody for theranostics in CD30-positive lymphoma.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Apr;52(5):1751-1763. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-07022-z. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39688699
-
[Radioimmunotherapy of lymphomas and leukemias].Pathol Biol (Paris). 1998 May;46(5):341-5. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1998. PMID: 9769896 Review. French.
-
Anti-CD30 antibody-based therapy.Curr Opin Oncol. 2000 Nov;12(6):588-93. doi: 10.1097/00001622-200011000-00012. Curr Opin Oncol. 2000. PMID: 11085459 Review.
Cited by
-
Noninvasive Trafficking of Brentuximab Vedotin and PET Imaging of CD30 in Lung Cancer Murine Models.Mol Pharm. 2018 Apr 2;15(4):1627-1634. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b01168. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29537283 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding CD30 biology and therapeutic targeting: a historical perspective providing insight into future directions.Blood Cancer J. 2017 Sep 8;7(9):e603. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2017.85. Blood Cancer J. 2017. PMID: 28885612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astatine-211 and actinium-225: two promising nuclides in targeted alpha therapy.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Nov 25;57(3):327-343. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024206. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 39587859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-CD30 Antibodies for Hodgkin lymphoma.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2010 Jul;5(3):140-7. doi: 10.1007/s11899-010-0053-y. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2010. PMID: 20446121 Review.
-
Targeting of a developmentally regulated epitope of CD43 for the treatment of acute leukemia.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 Dec;60(12):1697-706. doi: 10.1007/s00262-011-1066-7. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011. PMID: 21710258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koon HB, Junghans RP. Curr Opin Oncol. 2000;12:588–593. - PubMed
-
- de Bruin PC, Gruss HJ, van der Valk P, Willemze R, Meijer CJ. Leukemia. 1995;9:1620–1627. - PubMed
-
- Durkop H, Foss HD, Eitelbach F, Anagnostopoulos I, Latza U, Pileri S, Stein H. J Pathol. 2000;190:613–618. - PubMed
-
- Higgins JP, Warnke RA. Am J Clin Pathol. 1999;112:241–247. - PubMed
-
- Kadin ME. Semin Dermatol. 1991;10:164–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

