Characterization of Agrobacterium tumefaciens DNA ligases C and D
- PMID: 17488851
- PMCID: PMC1920237
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm145
Characterization of Agrobacterium tumefaciens DNA ligases C and D
Abstract
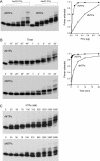
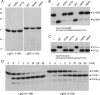
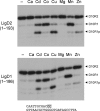
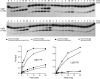
Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes a single NAD+-dependent DNA ligase and six putative ATP-dependent ligases. Two of the ligases are homologs of LigD, a bacterial enzyme that catalyzes end-healing and end-sealing steps during nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ). Agrobacterium LigD1 and AtuLigD2 are composed of a central ligase domain fused to a C-terminal polymerase-like (POL) domain and an N-terminal 3'-phosphoesterase (PE) module. Both LigD proteins seal DNA nicks, albeit inefficiently. The LigD2 POL domain adds ribonucleotides or deoxyribonucleotides to a DNA primer-template, with rNTPs being the preferred substrates. The LigD1 POL domain has no detectable polymerase activity. The PE domains catalyze metal-dependent phosphodiesterase and phosphomonoesterase reactions at a primer-template with a 3'-terminal diribonucleotide to yield a primer-template with a monoribonucleotide 3'-OH end. The PE domains also have a 3'-phosphatase activity on an all-DNA primer-template that yields a 3'-OH DNA end. Agrobacterium ligases C2 and C3 are composed of a minimal ligase core domain, analogous to Mycobacterium LigC (another NHEJ ligase), and they display feeble nick-sealing activity. Ligation at DNA double-strand breaks in vitro by LigD2, LigC2 and LigC3 is stimulated by bacterial Ku, consistent with their proposed function in NHEJ.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of Mycobacterium smegmatis PolD2 and PolD1 as RNA/DNA polymerases homologous to the POL domain of bacterial DNA ligase D.Biochemistry. 2012 Dec 21;51(51):10147-58. doi: 10.1021/bi301202e. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 23198659 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial nonhomologous end joining ligases preferentially seal breaks with a 3'-OH monoribonucleotide.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 28;283(13):8331-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705476200. Epub 2008 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18203718 Free PMC article.
-
Essential constituents of the 3'-phosphoesterase domain of bacterial DNA ligase D, a nonhomologous end-joining enzyme.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 7;280(40):33707-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506838200. Epub 2005 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16046407
-
DNA and RNA ligases: structural variations and shared mechanisms.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Feb;18(1):96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2007.12.008. Epub 2008 Feb 8. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 18262407 Review.
-
LigD: A Structural Guide to the Multi-Tool of Bacterial Non-Homologous End Joining.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Nov 25;8:787709. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.787709. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34901162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Solution structure and DNA-binding properties of the phosphoesterase domain of DNA ligase D.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Mar;40(5):2076-88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr950. Epub 2011 Nov 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22084199 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Mycobacterium smegmatis PolD2 and PolD1 as RNA/DNA polymerases homologous to the POL domain of bacterial DNA ligase D.Biochemistry. 2012 Dec 21;51(51):10147-58. doi: 10.1021/bi301202e. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 23198659 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-inducible NHEJ in bacteria: function in DNA repair and acquisition of heterologous DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Feb 20;47(3):1335-1349. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1212. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30517704 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of ATP-bound DNA ligase D in a closed domain conformation reveal a network of amino acid and metal contacts to the ATP phosphates.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 29;294(13):5094-5104. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007445. Epub 2019 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30718283 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin organization and radio resistance in the bacterium Gemmata obscuriglobus.J Bacteriol. 2009 Mar;191(5):1439-45. doi: 10.1128/JB.01513-08. Epub 2008 Dec 12. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19074379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lehman IR. DNA ligase: structure, mechanism, and function. Science. 1974;186:790–797. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson A, Day J, Bowater R. Bacterial DNA ligases. Mol. Microbiol. 2001;40:1241–1248. - PubMed
-
- Singleton MR, Håkansson K, Timson DJ, Wigley DB. Structure of the adenylation domain of an NAD+-dependent DNA ligase. Structure. 1999;7:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Gajiwala K, Pinko C. Structural rearrangement accompanying NAD+ synthesis within a bacterial DNA ligase crystal. Structure. 2004;12:1449–1459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

