Characterization of human pre-elafin mutants: full antipeptidase activity is essential to preserve lung tissue integrity in experimental emphysema
- PMID: 17489739
- PMCID: PMC2267300
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070020
Characterization of human pre-elafin mutants: full antipeptidase activity is essential to preserve lung tissue integrity in experimental emphysema
Abstract
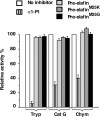
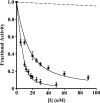
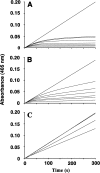
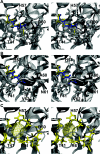
Pre-elafin is a tight-binding inhibitor of neutrophil elastase and myeloblastin; two enzymes thought to contribute to tissue damage in lung emphysema. Previous studies have established that pre-elafin is also an effective anti-inflammatory molecule. However, it is not clear whether both functions are linked to the antipeptidase activity of pre-elafin. As a first step toward elucidating the structure/function relationship of this protein, we describe here the construction and characterization of pre-elafin variants with attenuated antipeptidase potential. In these mutants, the P1' methionine residue of the inhibitory loop is replaced by either a lysine (pre-elafinM25K) or a glycine (pre-elafinM25G) residue. Both mutated variants are stable and display biochemical properties undistinguishable from WT (wild-type) pre-elafin. However, compared with WT pre-elafin, their inhibitory constants are increased by one to four orders of magnitude toward neutrophil elastase, myeloblastin and pancreatic elastase, depending on the variants and enzymes tested. As suggested by molecular modelling, this attenuated inhibitory potential correlates with decreased van der Waals interactions between the variants and the enzymes S1' subsite. In elastase-induced experimental emphysema in mice, only WT pre-elafin protected against tissue destruction, as assessed by the relative airspace enlargement measured using lung histopathological sections. Pre-elafin and both mutants prevented transient neutrophil alveolitis. However, even the modestly affected pre-elafinM25K mutant, as assayed in vitro with small synthetic substrates, was a poor inhibitor of the neutrophil elastase and myeloblastin elastolytic activity measured with insoluble elastin. We therefore conclude that full antipeptidase activity of pre-elafin is essential to protect against lung tissue lesions in this experimental model.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of an elastase-specific inhibitor elafin complexed with porcine pancreatic elastase determined at 1.9 A resolution.Biochemistry. 1996 Sep 10;35(36):11570-6. doi: 10.1021/bi960900l. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8794736
-
Neutrophil influx into the lungs of beige mice is followed by elastolytic damage and emphysema.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999 Feb;20(2):264-9. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.20.2.3235. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 9922217
-
Oxidized elafin and trappin poorly inhibit the elastolytic activity of neutrophil elastase and proteinase 3.FEBS J. 2005 Nov;272(22):5883-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04988.x. FEBS J. 2005. PMID: 16279952
-
Therapeutic potential of human elafin.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Oct;39(5):1450-4. doi: 10.1042/BST0391450. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21936832 Review.
-
Structure-function relationship of serine protease-protein inhibitor interaction.Acta Biochim Pol. 2001;48(2):419-28. Acta Biochim Pol. 2001. PMID: 11732612 Review.
Cited by
-
Human pre-elafin inhibits a Pseudomonas aeruginosa-secreted peptidase and prevents its proliferation in complex media.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Feb;52(2):483-90. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00585-07. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18025118 Free PMC article.
-
Protease inhibitors derived from elafin and SLPI and engineered to have enhanced specificity towards neutrophil serine proteases.Protein Sci. 2009 Mar;18(3):579-94. doi: 10.1002/pro.64. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19241385 Free PMC article.
-
Proteases and Their Inhibitors in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.J Clin Med. 2018 Aug 28;7(9):244. doi: 10.3390/jcm7090244. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30154365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-glycan analysis of human α1-antitrypsin produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells.Glycoconj J. 2013 Jul;30(5):537-47. doi: 10.1007/s10719-012-9453-7. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Glycoconj J. 2013. PMID: 23065139
-
The serine protease inhibitor elafin maintains normal growth control by opposing the mitogenic effects of neutrophil elastase.Oncogene. 2015 Jul;34(27):3556-67. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.284. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25195861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spurzem J. R., Rennard S. I. Pathogenesis of COPD. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005;26:142–153. - PubMed
-
- Thurlbeck W. M. Pathology of chronic airflow obstruction. In: Cherniack N. S., editor. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co.; 1991. pp. 3–20.
-
- Reid P. T., Sallenave J. M. Neutrophil-derived elastases and their inhibitors: potential role in the pathogenesis of lung disease. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2001;2:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Belvisi M. G., Bottomley K. M. The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in the pathophysiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): a therapeutic role for inhibitors of MMPs? Inflamm. Res. 2003;52:95–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

