Anaplastic lymphoma kinase is expressed in different subtypes of human breast cancer
- PMID: 17490616
- PMCID: PMC1945107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.137
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase is expressed in different subtypes of human breast cancer
Abstract
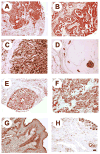
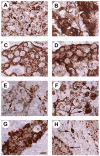
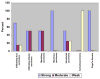
Pleiotrophin (PTN, Ptn) is an 18kDa cytokine expressed in human breast cancers. Since inappropriate expression of Ptn stimulates progression of breast cancer in transgenic mice and a dominant negative PTN reverses the transformed phenotype of human breast cancer cells that inappropriately express Ptn, it is suggested that constitutive PTN signaling in breast cancer cells that inappropriately express Ptn activates pathways that promote a more aggressive breast cancer phenotype. Pleiotrophin signals by inactivating its receptor, the receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase (RPTP)beta/zeta, and, recently, PTN was found to activate anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) through the PTN/RPTPbeta/zeta signaling pathway in PTN-stimulated cells, not through a direct interaction of PTN with ALK and thus not through the PTN-enforced dimerization of ALK. Since full-length ALK is activated in different malignant cancers and activated ALK is a potent oncogenic protein, we examined human breast cancers to test the possibility that ALK may be expressed in breast cancers and potentially activated through the PTN/RPTPbeta/zeta signaling pathway; we now demonstrate that ALK is strongly expressed in different histological subtypes of human breast cancer; furthermore, ALK is expressed in both nuclei and cytoplasm and, in the ;;dotted" pattern characteristic of ALK fusion proteins in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. This study thus supports the possibility that activated ALK may be important in human breast cancers and potentially activated either through the PTN/RPTPbeta/zeta signaling pathway, or, alternatively, as an activated fusion protein to stimulate progression of breast cancer in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase (RPTP)beta/zeta is expressed in different subtypes of human breast cancer.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Oct 12;362(1):5-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.06.050. Epub 2007 Jun 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17706593 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase is activated through the pleiotrophin/receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta signaling pathway: an alternative mechanism of receptor tyrosine kinase activation.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28683-28690. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704505200. Epub 2007 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17681947
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: "Ligand Independent Activation" mediated by the PTN/RPTPβ/ζ signaling pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1834(10):2219-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23777859 Review.
-
Fyn is a downstream target of the pleiotrophin/receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta-signaling pathway: regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of Fyn by pleiotrophin.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Jul 8;332(3):664-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.05.007. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 15925565
-
Pleiotrophin, a multifunctional tumor promoter through induction of tumor angiogenesis, remodeling of the tumor microenvironment, and activation of stromal fibroblasts.Cell Cycle. 2007 Dec 1;6(23):2877-83. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.23.5090. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 18156802 Review.
Cited by
-
Menin represses malignant phenotypes of melanoma through regulating multiple pathways.J Cell Mol Med. 2011 Nov;15(11):2353-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01222.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21129151 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotrophin (PTN) expression and function and in the mouse mammary gland and mammary epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047876. Epub 2012 Oct 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23077670 Free PMC article.
-
Association of an anaplastic lymphoma kinase pathway signature with cell de-differentiation, neoadjuvant chemotherapy response, and recurrence risk in breast cancer.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020 Sep;40(9):422-434. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12038. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32822101 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Posterior Cranial Fossa Tumors: A Scoping Review of Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 2;16(3):650. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030650. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339401 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: role in cancer pathogenesis and small-molecule inhibitor development for therapy.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009 Mar;9(3):331-56. doi: 10.1586/14737140.9.3.331. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 19275511 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sjoblom T, Jones S, Wood LD, Parsons DW, Lin J, Barber TD, Mandelker D, Leary RJ, Ptak J, Silliman N, Szabo S, Buckhaults P, Farrell C, Meeh P, Markowitz SD, Willis J, Dawson D, Willson JK, Gazdar AF, Hartigan J, Wu L, Liu C, Parmigiani G, Park BH, Bachman KE, Papadopoulos N, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW, Velculescu VE. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science. 2006;314:268–274. - PubMed
-
- Iwahara T, Fujimoto J, Wen D, Cupples R, Bucay N, Arakawa T, Mori S, Ratzkin B, Yamamoto T. Molecular characterization of ALK, a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed specifically in the nervous system. Oncogene. 1997;14:439–449. - PubMed
-
- Mourali J, Benard A, Lourenco FC, Monnet C, Greenland C, Moog-Lutz C, Racaud-Sultan C, Gonzalez-Dunia D, Vigny M, Mehlen P, Delsol G, Allouche M. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase is a dependence receptor whose proapoptotic functions are activated by caspase cleavage. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:6209–6222. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL, Look AT. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science. 1994;263:1281–1284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

