Injury and nucleotides induce phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor: MMP and HB-EGF dependent pathway
- PMID: 17490650
- PMCID: PMC2577227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.03.009
Injury and nucleotides induce phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor: MMP and HB-EGF dependent pathway
Abstract
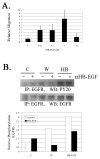
The early events that occur rapidly after injury trigger signal cascades that are essential for proper wound closure of corneal epithelial cells. We hypothesize that injury releases ATP, which stimulates purinergic receptors and elicits the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine residues and subsequent cell migration by a MMP and HB-EGF dependent pathway. We demonstrated that the inhibition of purinergic receptors with the antagonist, Reactive Blue 2, abrogated the phosphorylation of EGFR and ERK. Pre-incubation of cells with the EGFR kinase inhibitor, AG1478, and subsequent stimulation by injury or ATP resulted in a decrease in phosphorylation of EGFR and migration. Furthermore, downregulation of EGFR by siRNA, inhibited the EGF-induced intracellular Ca(2+) wave. However, the response to injury and ATP was retained indicating the presence of two signaling pathways. Inhibition with either CRM197 or TIMP-3 decreased injury and nucleotide-induced phosphorylation of both EGFR and ERK. Incubation in the presence of a functional blocking antibody to HB-EGF also resulted in a decrease in the phosphorylation of EGFR. In addition, cell migration was inhibited by CRM197 and rescued when cells were incubated with HB-EGF. We showed that injury-induced phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues and found that a similar pattern of phosphorylation was induced by trinucleotides. These studies indicate that injury-induced purinergic receptor activation leads to phosphorylation of EGFR, ERK and migration.
Figures





References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling: pathophysiological roles. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1998;78:113–45. - PubMed
-
- Andreev J, Galisteo ML, Kranenburg O, Logan SK, Chiu ES, Okigaki M, Cary LA, Moolenaar WH, Schlessinger J. Src and Pyk2 Mediate G-protein-coupled Receptor Activation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) but are not Required for Coupling to the Mitogen-activated Protein (MAP) Kinase Signaling Cascade. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:20130–20135. - PubMed
-
- Araki-Sasaki K, Ohashi Y, Sasabe T, Hayashi K, Watanabe H, Tano Y, Handa H. An SV40-immortalized human corneal epithelial cell line and its characterization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995;36:614–621. - PubMed
-
- Block ER, Matela A, SundarRaj N, Iszkula ER, Klarlund JK. Wounding induces motility in sheets of corneal epithelial cells through loss of spatial constraints: role of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:24307–24312. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. The past, present and future of purine nucleotides as signalling molecules. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:1127–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

