Dendritic distributions of dopamine D1 receptors in the rat nucleus accumbens are synergistically affected by startle-evoking auditory stimulation and apomorphine
- PMID: 17490822
- PMCID: PMC1978178
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.04.005
Dendritic distributions of dopamine D1 receptors in the rat nucleus accumbens are synergistically affected by startle-evoking auditory stimulation and apomorphine
Abstract
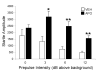
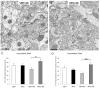
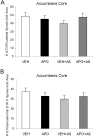
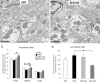
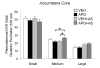
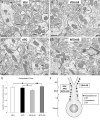
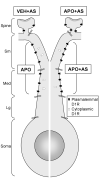
Prepulse inhibition of the startle response to auditory stimulation (AS) is a measure of sensorimotor gating that is disrupted by the dopamine D1/D2 receptor agonist, apomorphine. The apomorphine effect on prepulse inhibition is ascribed in part to altered synaptic transmission in the limbic-associated shell and motor-associated core subregions of the nucleus accumbens (Acb). We used electron microscopic immunolabeling of dopamine D1 receptors (D1Rs) in the Acb shell and core to test the hypothesis that region-specific redistribution of D1Rs is a short-term consequence of AS and/or apomorphine administration. Thus, comparisons were made in the Acb of rats killed 1 h after receiving a single s.c. injection of vehicle (VEH) or apomorphine (APO) alone or in combination with startle-evoking AS (VEH+AS, APO+AS). In both regions of all animals, the D1R immunoreactivity was present in somata and large, as well as small, presumably more distal dendrites and dendritic spines. In the Acb shell, compared with the VEH+AS group, the APO+AS group had more spines containing D1R immunogold particles, and these particles were more prevalent on the plasma membranes. This suggests movement of D1Rs from distal dendrites to the plasma membrane of dendritic spines. Small- and medium-sized dendrites also showed a higher plasmalemmal density of D1R in the Acb shell of the APO+AS group compared with the APO group. In the Acb core, the APO+AS group had a higher plasmalemmal density of D1R in medium-sized dendrites compared with the APO or VEH+AS group. Also in the Acb core, D1R-labeled dendrites were significantly smaller in the VEH+AS group compared with all other groups. These results suggest that alerting stimuli and apomorphine synergistically affect distributions of D1R in Acb shell and core. Thus adaptations in D1R distribution may contribute to sensorimotor gating deficits that can be induced acutely by apomorphine or develop over time in schizophrenia.
Figures

References
-
- Bakshi VP, Tricklebank M, Neijt HC, Lehmann-Masten V, Geyer MA. Disruption of prepulse inhibition and increases in locomotor activity by competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;288:643–652. - PubMed
-
- Braff DL, Grillon C, Geyer MA. Gating and habituation of the startle reflex in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992;49:206–215. - PubMed
-
- Brog JS, Salyapongse A, Deutch AY, Zahm DS. The patterns of afferent innervation of the core and shell in the “accumbens” part of the rat ventral striatum: immunohistochemical detection of retrogradely transported fluoro-gold. J Comp Neurol. 1993;338:255–278. - PubMed
-
- Carey MP, Diewald LM, Esposito FJ, Pellicano MP, Gironi Carnevale UA, Sergeant JA, Papa M, Sadile AG. Differential distribution, affinity and plasticity of dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors in the target sites of the mesolimbic system in an animal model of ADHD. Behav Brain Res. 1998;94:173–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

