Delinquency as a mediator of the relation between negative affectivity and adolescent alcohol use disorder
- PMID: 17490823
- PMCID: PMC2629998
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2007.04.011
Delinquency as a mediator of the relation between negative affectivity and adolescent alcohol use disorder
Abstract
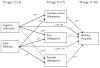
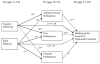
This investigation examined mediators of the longitudinal relation between negative affectivity and the development of problematic drinking behavior in adolescent boys and girls. In the present study, 499 early adolescents completed inventories of negative affectivity, attitudes toward delinquency, personal delinquency, and affiliation with delinquent peers. Positive attitudes toward delinquency emerged as the most consistent mediator and strongly predicted drinking frequency in various situations. Compared with personal delinquency, both attitudes toward delinquency and peer delinquency were superior predictors of affect-related drinking. Our results also demonstrated that positive attitudes toward delinquency mediated the relation between negative affectivity and later development of an alcohol use disorder. These findings suggest that a proneness to unpleasant affect impacts adolescent drinking by heightening risk for general rejection of normative behavior, rather than by increasing drinking as a means of managing affect. The importance and implications of testing delinquency variables together in the same model are discussed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Do alcohol expectancies and peer delinquency/substance use mediate the relationship between impulsivity and drinking behaviour in adolescence?Alcohol Alcohol. 2004 May-Jun;39(3):213-9. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agh048. Alcohol Alcohol. 2004. PMID: 15082458
-
Vulnerability to peer influence: a moderated mediation study of early adolescent alcohol use initiation.Addict Behav. 2011 Jul;36(7):729-36. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2011.02.008. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Addict Behav. 2011. PMID: 21420241 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting early adolescent offending with criminal victimization and delinquent peer associations by way of negative attitudes toward the police.Law Hum Behav. 2019 Dec;43(6):517-526. doi: 10.1037/lhb0000341. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Law Hum Behav. 2019. PMID: 31282692
-
Gender differences in factors influencing alcohol use and drinking progression among adolescents.Clin Psychol Rev. 2009 Aug;29(6):535-47. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2009.06.003. Epub 2009 Jun 11. Clin Psychol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19592147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Movies and juvenile delinquency: an overview.Adolescence. 1991 Spring;26(101):121-32. Adolescence. 1991. PMID: 2048467 Review.
Cited by
-
Adolescent brain development and the risk for alcohol and other drug problems.Neuropsychol Rev. 2010 Dec;20(4):398-413. doi: 10.1007/s11065-010-9146-6. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Neuropsychol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20953990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between perceptions of school climate and internet gaming disorder of teenage students: A moderated mediation model.Front Psychol. 2022 Aug 8;13:917872. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.917872. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36003106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achenbach T. Manual for the Youth Self Report and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT: Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont; 1991.
-
- Achenbach T, Edelbrock C. Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist and Revised Child Behavioral Profile. Burlington, VT: Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont; 1983.
-
- Akers RL. Deviant Behavior: A Social Learning Approach. 2nd. Wadsworth; Belmont: 1977.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd Edition-Revised. Washington D.C.: Author; 1987.
-
- Annis HM, Graham JM, Davis CS. Inventory of Drinking Situations (IDS): User's Guide. Toronto: Addiction Research Foundation; 1987.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

