GILZ mediates the antiproliferative activity of glucocorticoids by negative regulation of Ras signaling
- PMID: 17492054
- PMCID: PMC1865030
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI30724
GILZ mediates the antiproliferative activity of glucocorticoids by negative regulation of Ras signaling
Abstract
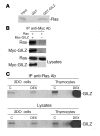
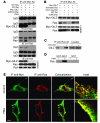
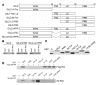
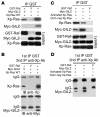
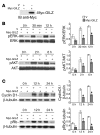
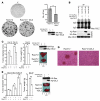
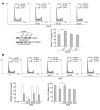
Tsc22d3 coding for glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) was initially identified as a dexamethasone-responsive gene involved in the control of T lymphocyte activation and apoptosis. However, the physiological role of this molecule and its function in the biological activity of glucocorticoids (GCs) has not been clarified. Here, we demonstrate that GILZ interacts directly with Ras in vitro and in vivo as shown by GILZ and Ras coimmunoprecipitation and colocalization upon PMA activation in primary mouse spleen T lymphocytes and thymus cells. The analysis of GILZ mutants showed that they bound Ras through the tuberous sclerosis complex box (TSC) and, depending on the Ras activation level, formed a trimeric complex with Ras and Raf, which we previously identified as a GILZ binder. As a consequence of these interactions, GILZ diminished the activation of Ras and Raf downstream targets including ERK1/2, AKT/PKB serine/threonine kinase, and retinoblastoma (Rb) phosphorylation and cyclin D1 expression, leading to inhibition of Ras- and Raf-dependent cell proliferation and Ras-induced NIH-3T3 transformation. GILZ silencing resulted in an increase in concanavalin A-induced T cell proliferation and, most notably, inhibition of dexamethasone antiproliferative effects. Together, these findings indicate that GILZ serves as a negative regulator of Ras- and Raf-induced proliferation and is an important mediator of the antiproliferative effect of GCs.
Figures
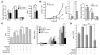
Similar articles
-
[GILZ (glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper), a mediator of the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive activity of glucocorticoids].Ann Ig. 2010 Jan-Feb;22(1 Suppl 1):53-9. Ann Ig. 2010. PMID: 20701225 Italian.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ): a new important mediator of glucocorticoid action.FASEB J. 2009 Nov;23(11):3649-58. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-134684. Epub 2009 Jun 30. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19567371 Review.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper is an endogenous antiinflammatory mediator in arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Sep;62(9):2651-61. doi: 10.1002/art.27566. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 20496421
-
Dexamethasone and IL-10 stimulate glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper synthesis by human mast cells.Allergy. 2006 Jul;61(7):886-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01065.x. Allergy. 2006. PMID: 16792589
-
Implicating the Role of GILZ in Glucocorticoid Modulation of T-Cell Activation.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 7;10:1823. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01823. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31440237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene expression profiles of dental follicle cells before and after osteogenic differentiation in vitro.Clin Oral Investig. 2009 Dec;13(4):383-91. doi: 10.1007/s00784-009-0260-x. Epub 2009 Feb 28. Clin Oral Investig. 2009. PMID: 19252934
-
Role of GILZ in immune regulation, glucocorticoid actions and rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011 Jun;7(6):340-8. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2011.59. Epub 2011 May 10. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21556028 Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of kinases downstream of the T cell receptor: another immunomodulatory mechanism of glucocorticoids.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014 Jul 3;15:35. doi: 10.1186/2050-6511-15-35. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24993777 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) in Cardiovascular Health and Disease.Cells. 2021 Aug 21;10(8):2155. doi: 10.3390/cells10082155. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of Glucocorticoid-induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) Contributes to Anti-inflammatory Effects of the Natural Product Curcumin in Macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 28;291(44):22949-22960. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.733253. Epub 2016 Sep 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27629417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Payne D.N., Adcock I.M. Molecular mechanisms of corticosteroid actions. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2001;2:145–150. - PubMed
-
- De Bosscher K., Vanden Berghe W., Haegeman G. Mechanisms of anti-inflammatory action and of immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: negative interference of activated glucocorticoid receptor with transcription factors. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000;109:16–22. - PubMed
-
- Adcock I.M. Glucocorticoid-regulated transcription factors. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001;14:211–219. - PubMed
-
- Wikstrom A.C. Glucocorticoid action and novel mechanisms of steroid resistance: role of glucocorticoid receptor-interacting proteins for glucocorticoid responsiveness. J. Endocrinol. 2003;178:331–337. - PubMed
-
- Almawi W.Y., Abou Jaoude M.M., Li X.C. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms of glucocorticoid antiproliferative effects. Hematol. Oncol. 2002;20:17–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

