Tolerance to coxibs in patients with intolerance to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): a systematic structured review of the literature
- PMID: 17492455
- PMCID: PMC1910889
- DOI: 10.1007/s00403-007-0757-6
Tolerance to coxibs in patients with intolerance to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): a systematic structured review of the literature
Abstract
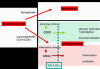
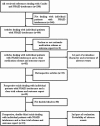
Adverse events triggered by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are among the most common drug-related intolerance reactions in medicine; they are possibly related to inhibition of cyclooxygenase-1. Coxibs, preferentially inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2, may therefore represent safe alternatives in patients with NSAID intolerance. We reviewed the literature in a systematic and structured manner to identify and evaluate studies on the tolerance of coxibs in patients with NSAID intolerance. We searched MEDLINE (1966-2006), the COCHRANE LIBRARY (4th Issue 2006) and EMBASE (1966-2006) up to December 9, 2006, and analysed all publications included using a predefined evaluation sheet. Symptoms and severity of adverse events to coxibs were analysed based on all articles comprising such information. Subsequently, the probability for adverse events triggered by coxibs was determined on analyses of double-blind prospective trials only. Among 3,304 patients with NSAID intolerance, 119 adverse events occurred under coxib medication. All adverse events, except two, have been allergic/urticarial in nature; none was lethal, but two were graded as life-threatening (grade 4). The two non-allergic adverse events were described as a grade 1 upper respiratory tract haemorrhage, and a grade 1 gastrointestinal symptom, respectively. In 13 double-blind prospective studies comprising a total of 591 patients with NSAID intolerance, only 13 adverse reactions to coxib provocations were observed. The triggering coxibs were rofecoxib (2/286), celecoxib (6/208), etoricoxib (4/56), and valdecoxib (1/41). This review documents the good tolerability of coxibs in patients with NSAID intolerance, for whom access to this class of drugs for short-term treatment of pain and inflammation is advantageous.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for acute gout.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 9;12(12):CD010120. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010120.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34882311 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Oct;10(38):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10380. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17018227
-
WITHDRAWN: Non-aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for treating osteoarthritis of the knee.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;2006(1):CD000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000142.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. PMID: 17636601 Free PMC article.
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents to induce regression and prevent the progression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 12;2(2):CD004121. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004121.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29431861 Free PMC article.
-
Single-dose intravenous diclofenac for acute postoperative pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 28;8(8):CD012498. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012498.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30153336 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Safe administration of celecoxib to a patient with repeated episodes of nephrotic syndrome induced by NSAIDs.Clin Drug Investig. 2011;31(5):351-5. doi: 10.1007/BF03256934. Clin Drug Investig. 2011. PMID: 21271751
-
A drug repurposing screen reveals dopamine signaling as a critical pathway underlying potential therapeutics for the rare disease DPAGT1-CDG.PLoS Genet. 2024 Oct 28;20(10):e1011458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011458. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39466823 Free PMC article.
-
Flupirtine is a safe alternative drug in patients with hypersensitivity to NSAIDs.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;67(9):961-3. doi: 10.1007/s00228-011-1022-7. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21387166 No abstract available.
-
The selective COX-2 inhibitor Etoricoxib reduces acute inflammatory markers in a model of neurogenic laryngitis but loses its efficacy with prolonged treatment.Inflamm Res. 2010 Sep;59(9):743-53. doi: 10.1007/s00011-010-0185-5. Epub 2010 Mar 28. Inflamm Res. 2010. PMID: 20349107
-
Tolerance to alternative cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug hypersensitive patients.Clin Transl Allergy. 2013 Jun 24;3(1):20. doi: 10.1186/2045-7022-3-20. Clin Transl Allergy. 2013. PMID: 23799898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/s00063-003-1251-3', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/s00063-003-1251-3'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12721666', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12721666/'}]}
- Ahlbach S, Usadel KH, Kaufmann R, Boehncke WH (2003) The selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib is a safe alternative in patients with pseudo-allergic reactions to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Med Klin (Munich) 98:242–244 - PubMed
-
- None
- Andri L (2001) Safety of celecoxib in patients with ASA/NSAIDs sensitivity (abstract). Allergy 56:223
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1034/j.1398-9995.2001.00300.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1398-9995.2001.00300.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11551261', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11551261/'}]}
- Asero R (2001) Tolerability of rofecoxib. Allergy Eur J Allergy Clin Immunol 56:916–917 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12861852', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12861852/'}]}
- Asero R (2003) Chronic urticaria with multiple NSAID intolerance: Is tramadol always a safe alternative analgesic? J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 13:56–59 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.2228.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.2228.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15969659', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15969659/'}]}
- Asero R (2005) Oral aspirin challenges in patients with a history of intolerance to single non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin Exp Allergy 35:713–716 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

