The chondroitin sulfate form of invariant chain trimerizes with conventional invariant chain and these complexes are rapidly transported from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface
- PMID: 17492940
- PMCID: PMC1948987
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070446
The chondroitin sulfate form of invariant chain trimerizes with conventional invariant chain and these complexes are rapidly transported from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface
Abstract
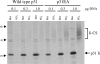
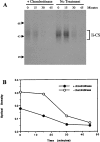
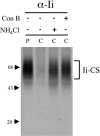
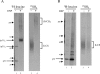
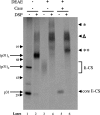
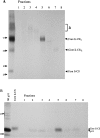
Targeting of MHCII-invariant chain complexes from the trans-Golgi network to endosomes is mediated by two di-leucine-based signals present in the cytosolic domain of invariant chain. Generation of this endosomal targeting signal is also dependent on multimerization of the invariant chain cytosolic domain sequences, mediated through assembly of invariant chain into homotrimers. A small subset of invariant chain is modified by the addition of chondroitin sulfate and is expressed on the cell surface in association with MHCII. In the present study, we have followed the biosynthetic pathway and route of intracellular transport of this proteoglycan form of invariant chain. We found that the efficiency of chondroitin sulfate modification can be increased by altering the invariant chain amino acid sequence around Ser-201 to the xylosylation consensus sequence. Our results also indicate that, following sulfation, the proteoglycan form is transported rapidly from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface and is degraded following internalization into an endocytic compartment. Invariant chain-chondroitin sulfate is present in invariant chain trimers that also include conventional non-proteoglycan forms of invariant chain. These data indicate that invariant chain-chondroitin sulfate-containing complexes are transported rapidly from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface in spite of the presence of an intact endosomal localization signal. Furthermore, these results suggest that invariant chain-chondroitin sulfate may play an important role in the generation of cell-surface pools of invariant chain that can serve as receptors for CD44 and macrophage migration inhibitory factor.
Figures
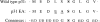
References
-
- Hiltbolt E. M., Roche P. A. Trafficking of MHC class II molecules in the late secretory pathway. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002;14:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Bakke O., Dobberstein B. MHC class II-associated invariant chain contains a sorting signal for endosomal compartments. Cell. 1990;63:707–716. - PubMed
-
- Lotteau V., Teyton L., Peleraux A., Nilsson T., Karlsson L., Schmid S., Quaranta V., Peterson P. Intracellular transport of class II MHC molecules directed by invariant chain. Nature. 1990;348:600–605. - PubMed
-
- Shachar I., Flavell R. Requirement for invariant chain in B cell maturation and function. Science. 1996;274:106–108. - PubMed
-
- Benlagha K., Park S.-H., Guinamard R., Forestier C., Karlsson L., Chang C.-H., Bendelac A. Mechanisms governing B cell development defects in invariant chain-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 2004;172:2076–2083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

