Multi-level modeling to explain methamphetamine use among gay and bisexual men
- PMID: 17493056
- PMCID: PMC8444233
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.01769.x
Multi-level modeling to explain methamphetamine use among gay and bisexual men
Abstract
Aim: The popularity of methamphetamine among gay men has been documented; however, few studies have examined the complex behavioral and psychological motivations behind methamphetamine use, particularly over time. This study aimed to (i) identify the trajectories for methamphetamine use; (ii) explore factors related to methamphetamine use; and (iii) determine factors which predict changes in usage over a year.
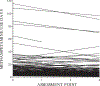
Design: This analysis utilized hierarchical linear modeling to identify the trajectories for methamphetamine use and explore factors related to patterns of methamphetamine use.
Participants: A sample of 293 gay and bisexual men who indicated methamphetamine use at baseline were drawn from Project BUMPS (Boys Using Multiple Party Substances), which was a longitudinal, mixed-methodologies study of 450 club drug-using gay and bisexual men.
Measurements: Participants were assessed via quantitative measures in four waves of data collection over the course of a year (baseline, 4, 8 and 12 months post-baseline).
Findings: Frequency of methamphetamine use is related to reliance on the drug to avoid unpleasant emotions and physical discomfort, outcome expectancies for use and combining the drug with Viagra. Those with higher levels of drug-related sensation-seeking and those who combine use with Viagra show more consistent use over time, although a decrease in use is noted for most of the sample.
Conclusions: Longitudinal analyses support the idea that methamphetamine is used by gay men to mask feelings of discomfort and to enhance sensations as well as sexual pleasure. Longitudinal non-intervention studies of drug use may have intervention-like effects.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Frosch D, Shoptaw S, Huber A, Rawson RA, Ling W Sexual HIV risk among gay and bisexual male methamphetamine abusers. J Subst Abuse Treat 1996; 13: 483–6. - PubMed
-
- Halkitis PN, Parsons JT, Stirratt MJ A double epidemic: crystal methamphetamine drug use in relation to HIV transmission among gay men. J Homosex 2001; 41: 17–35. - PubMed
-
- Halkitis PN, Parsons JT, Wilton L An exploratory study of contextual and situational factors related to methamphetamine use among gay and bisexual men in New York City. J Drug Issues 2003; 33: 413–32.
-
- Rawson RA, Anglin MD, Ling W Will the methamphetamine problem go away? J Addict Dis 2002; 21: 5–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical