Transmission dynamics of hepatitis E among swine: potential impact upon human infection
- PMID: 17493260
- PMCID: PMC1885244
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-6148-3-9
Transmission dynamics of hepatitis E among swine: potential impact upon human infection
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection is a zoonosis for which pigs play a role as a reservoir. In Japan, the infection has been enzootic in swine. Clarifying the detailed mechanisms of transmission within farms is required in order to facilitate an understanding of the age-specific patterns of infection, especially just prior to slaughter.
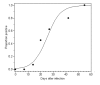
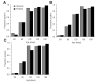
Results: Here we reanalyze a large-scale seroprevalence survey dataset from Japanese pig farms to estimate the force of infection. The forces of infection of swine HEV were estimated to be 3.45 (95% confidence interval: 3.17, 3.75), 2.68 (2.28, 3.14) and 3.11 (2.76, 3.50) [x10-2 per day] in Hokkaido, Honshu and Kyushu, respectively. The estimates with our model assumptions indicated that the average ages at infection ranged from 59.0-67.3 days and that the basic reproduction number, R0, was in the order of 4.02-5.17. Sensitivity analyses of age-specific incidence at different forces of infection revealed that a decline in the force of infection would elevate the age at infection and could increase the number of virus-excreting pigs at the age of 180 days.
Conclusion: Although our estimates imply that more than 95% of pigs are infected before the age of 150 days, the model shows that a decline in the force of infection could increase the risk of pig-to-human transmission. If the force of infection started to decline, it might be necessary to implement radical countermeasures (e.g. separation of uninfected pigs from infected herds beginning from the end of the suckling stage) to minimize the number of virus-positive pigs at the finishing stage.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Repeated cross-sectional sampling of pigs at slaughter indicates varying age of hepatitis E virus infection within and between pig farms.Vet Res. 2022 Jul 7;53(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01068-3. Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35799280 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus in pigs from different farming systems in The Netherlands.J Food Prot. 2014 Apr;77(4):640-2. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-13-302. J Food Prot. 2014. PMID: 24680077
-
Prevalence of antibodies to the hepatitis E virus in pigs from countries where hepatitis E is common or is rare in the human population.J Med Virol. 1999 Nov;59(3):297-302. J Med Virol. 1999. PMID: 10502259
-
[Hepatitis E as a zoonosis].Nihon Rinsho. 2004 Aug;62 Suppl 8:524-31. Nihon Rinsho. 2004. PMID: 15453377 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Swine hepatitis E virus: cross-species infection and risk in xenotransplantation.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003;278:185-216. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-55541-1_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12934945 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis E virus infection in macaca mulatta.Hepat Mon. 2011 Oct;11(10):852-3. doi: 10.5812/kowsar.1735143x.783. Hepat Mon. 2011. PMID: 22224088 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Repeated cross-sectional sampling of pigs at slaughter indicates varying age of hepatitis E virus infection within and between pig farms.Vet Res. 2022 Jul 7;53(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01068-3. Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35799280 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the risk of parvovirus B19 infection in blood donors and pregnant women in Japan.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 21;9(3):e92519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092519. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24658180 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Shedding in Pigs.Animals (Basel). 2022 Apr 20;12(9):1063. doi: 10.3390/ani12091063. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565491 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling the time-dependent transmission rate for porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) in pigs using data from serial transmission experiments.J R Soc Interface. 2009 Jan 6;6(30):39-50. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0210. J R Soc Interface. 2009. PMID: 18559313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson DA, Cheng RH. Hepatitis E: structure and molecular virology. In: Thomas H, Lemon S, Zuckerman A, editor. Viral hepatitis. Oxford: Blackwell; 2005. pp. 603–610.
-
- Labrique AB, Thomas DL, Stoszek SK, Nelson KE. Hepatitis E: an emerging infectious disease. Epidemiol Rev. 1999;21:162–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

