Role of G(q) protein in behavioral effects of the hallucinogenic drug 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane
- PMID: 17493641
- PMCID: PMC1987710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.03.013
Role of G(q) protein in behavioral effects of the hallucinogenic drug 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane
Abstract
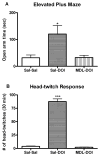
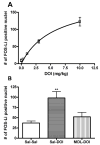
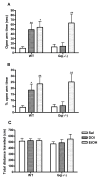
Extensive evidence suggests that 5-HT2 receptors may play a role in mental disorders including schizophrenia. In addition, several studies indicate that G(q)-coupled 5-HT(2A) receptors are likely targets for the initiation of events leading to the hallucinogenic behavior elicited by lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), (+/-)1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI), and related drugs. However, 5-HT(2A) receptors couple to other G proteins in addition to G(q) protein. To evaluate the role of the G(q) signaling pathway in DOI-induced behaviors, we utilized two behavioral models of 5-HT(2A) receptor activation: induction of head-twitches by DOI, a common response to hallucinogenic drugs in rodents, and DOI elicited anxiolytic-like effects in the elevated plus maze. Experimental subjects were genetically modified mice [Galpha(q)(-/-)] in which the G(q) alpha gene was eliminated. Galpha(q)(-/-) mice exhibited a decrease in DOI-induced head-twitches, when compared to wild-type littermates. In addition, the DOI-induced increase in anxiolytic-like behavior was abolished in Galpha(q)(-/-) mice. These results, combined with our finding that DOI-induced FOS expression in the medial prefrontal cortex was also eliminated in Galpha(q)(-/-) mice, suggests a key role for G(q) protein in hallucinogenic drug effects.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Head-twitch response in rodents induced by the hallucinogen 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine: a comprehensive history, a re-evaluation of mechanisms, and its utility as a model.Drug Test Anal. 2012 Jul-Aug;4(7-8):556-76. doi: 10.1002/dta.1333. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Drug Test Anal. 2012. PMID: 22517680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The serotonin 2C receptor potently modulates the head-twitch response in mice induced by a phenethylamine hallucinogen.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010 Apr;209(2):163-74. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-1784-0. Epub 2010 Feb 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20165943 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase C mediates (±)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI)-, but not lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)-elicited head bobs in rabbit medial prefrontal cortex.Brain Res. 2013 Jan 23;1491:98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.10.057. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23123701 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic and dopaminergic distinctions in the behavioral pharmacology of (±)-1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD).Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 Mar;101(1):69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.12.002. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012. PMID: 22197710 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of Hallucinogens with the Glutamatergic System: Permissive Network Effects Mediated Through Cortical Layer V Pyramidal Neurons.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:107-135. doi: 10.1007/7854_2017_480. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28831734 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms of serotonergic action of the HIV-1 antiretroviral efavirenz.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Aug;110:10-24. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.04.028. Epub 2016 May 6. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27157251 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of DOM-Induced Head-Twitch Response by mGluR2 Agonist/Inverse Agonist is Associated with 5-HT2AR-Mediated Gs Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2024 Mar;49(3):636-648. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04055-y. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 37989895
-
Enhanced function of prefrontal serotonin 5-HT(2) receptors in a rat model of psychiatric vulnerability.J Neurosci. 2010 Sep 8;30(36):12138-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3245-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20826676 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in intensity of serotonin syndrome caused by adverse interaction between monoamine oxidase inhibitors and serotonin reuptake blockers.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 Jul;39(8):1996-2007. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.49. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24577320 Free PMC article.
-
Head-twitch response in rodents induced by the hallucinogen 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine: a comprehensive history, a re-evaluation of mechanisms, and its utility as a model.Drug Test Anal. 2012 Jul-Aug;4(7-8):556-76. doi: 10.1002/dta.1333. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Drug Test Anal. 2012. PMID: 22517680 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aghajanian GK, Marek GJ. Serotonin and hallucinogens. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21:16S–23S. - PubMed
-
- Altman JL, Albert JM, Milstein SL, Greenberg I. Drugs as the discriminative events in humans. Psychopharmacol Commun. 1976;2:327–330. - PubMed
-
- Barnes NM, Sharp T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:1083–1152. - PubMed
-
- Barry H., 3rd Classification of drugs according to their discriminable effects in rats. Fed Proc. 1974;33:1814–1824. - PubMed
-
- Berg KA, Maayani S, Goldfarb J, Scaramellini C, Leff P, Clarke WP. Effector pathway-dependent relative efficacy at serotonin type 2A and 2C receptors: evidence for agonist-directed trafficking of receptor stimulus. Mol Pharmacol. 1998;54:94–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

