Structure-function analysis of the 3' phosphatase component of T4 polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase
- PMID: 17493655
- PMCID: PMC2761019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.03.059
Structure-function analysis of the 3' phosphatase component of T4 polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase
Abstract
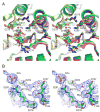
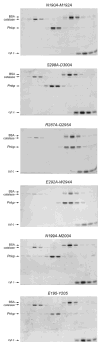
T4 polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase (Pnkp) exemplifies a family of bifunctional enzymes with 5'-kinase and 3' phosphatase activities that function in nucleic acid repair. T4 Pnkp is a homotetramer of a 301-aa polypeptide, which consists of an N-terminal kinase domain of the P-loop phosphotransferase superfamily and a C-terminal phosphatase domain of the DxD acylphosphatase superfamily. The homotetramer is formed via pairs of phosphatase-phosphatase and kinase-kinase homodimer interfaces. Here we identify four side chains-Asp187, Ser211, Lys258, and Asp277-that are required for 3' phosphatase activity. Alanine mutations at these positions abolished phosphatase activity without affecting kinase function or tetramerization. Conservative substitutions of asparagine or glutamate for Asp187 did not revive the 3' phosphatase, nor did arginine or glutamine substitutions for Lys258. Threonine in lieu of Ser211 and glutamate in lieu of Asp277 restored full activity, whereas asparagine at position 277 had no salutary effect. We report a 3.0 A crystal structure of the Pnkp tetramer, in which a sulfate ion is coordinated between Arg246 and Arg279 in a position that we propose mimics one of the penultimate phosphodiesters (5'NpNpNp-3') of the polynucleotide 3'-PO(4) substrate. The amalgam of mutational and structural data engenders a plausible catalytic mechanism for the phosphatase that includes covalent catalysis (via Asp165), general acid-base catalysis (via Asp167), metal coordination (by Asp165, Asp277 and Asp278), and transition state stabilization (via Lys258, Ser211, backbone amides, and the divalent cation). Other critical side chains play architectural roles (Arg176, Asp187, Arg213, Asp254). To probe the role of oligomerization in phosphatase function, we introduced six double-alanine cluster mutations at the phosphatase-phosphatase domain interface, two of which (R297A-Q295A and E292A-D300A) converted Pnkp from a tetramer to a dimer and ablated phosphatase activity.
Figures



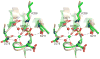
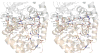
Similar articles
-
Mutational analysis defines the 5'-kinase and 3'-phosphatase active sites of T4 polynucleotide kinase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Feb 15;30(4):1073-80. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.4.1073. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11842120 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of RNA 2',3'-cyclic phosphate end healing by T4 polynucleotide kinase-phosphatase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan 7;41(1):355-65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks977. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23118482 Free PMC article.
-
Domain structure and mutational analysis of T4 polynucleotide kinase.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jul 20;276(29):26868-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103663200. Epub 2001 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11335730
-
Construction of linker-scanning mutations by oligonucleotide ligation.Methods Mol Biol. 1996;57:279-85. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-332-5:279. Methods Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8850014 Review. No abstract available.
-
Nuclease integrated kinase super assemblies (NiKs) and their role in RNA processing.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):183-190. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0749-9. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28929238 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of DNA3'pp5'G capping on repair reactions at DNA 3' ends.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Aug 5;111(31):11317-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1409203111. Epub 2014 Jul 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25049385 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution and structure of a bacterial Pnkp1-Rnl-Hen1 RNA repair complex.Nat Commun. 2015 Apr 17;6:6876. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7876. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25882814 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the phosphatase activity of polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase on single- and double-stranded DNA substrates.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 27;108(52):21022-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112036108. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22171004 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of Fcp1, an essential RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase.Mol Cell. 2008 Nov 21;32(4):478-90. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.09.021. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 19026779 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of bacterial LigD 3'-phosphoesterase unveils a DNA repair superfamily.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jul 20;107(29):12822-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005830107. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20616014 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker A, Hurwitz J. The enzymatic cleavage of phosphate termini from polynucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1967;242:936–950. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein NK, Williams RS, Rakovszky ML, Cui D, Green R, Galicia S, Koch CA, Cass CE, Durocher D, Weinfeld M, Glover JNM. The molecular architecture of the mammalian DNA repair enzyme, polynucleotide kinase. Mol Cell. 2005;17:657–670. - PubMed
-
- Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren GL. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 1998;D54:905–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

