Dissociation of eye and head components of gaze shifts by stimulation of the omnipause neuron region
- PMID: 17493925
- PMCID: PMC3639481
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00252.2007
Dissociation of eye and head components of gaze shifts by stimulation of the omnipause neuron region
Abstract
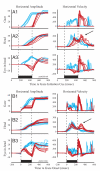
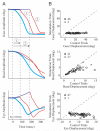
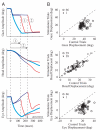
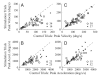
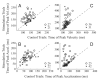
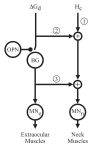
Natural movements often include actions integrated across multiple effectors. Coordinated eye-head movements are driven by a command to shift the line of sight by a desired displacement vector. Yet because extraocular and neck motoneurons are separate entities, the gaze shift command must be separated into independent signals for eye and head movement control. We report that this separation occurs, at least partially, at or before the level of pontine omnipause neurons (OPNs). Stimulation of the OPNs prior to and during gaze shifts temporally decoupled the eye and head components by inhibiting gaze and eye saccades. In contrast, head movements were consistently initiated before gaze onset, and ongoing head movements continued along their trajectories, albeit with some characteristic modulations. After stimulation offset, a gaze shift composed of an eye saccade, and a reaccelerated head movement was produced to preserve gaze accuracy. We conclude that signals subject to OPN inhibition produce the eye-movement component of a coordinated eye-head gaze shift and are not the only signals involved in the generation of the head component of the gaze shift.
Figures
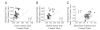



References
-
- Becker W. Saccades. In: Carpenter RHS, editor. Eye Movements. Macmillan; London: 1991. pp. 95–137.
-
- Becker W, Jürgens R. Gaze saccades to visual targets: does head movement change the metrics. In: Berthoz A, Graf W, Vidal PP, editors. The Head-Neck Sensory Motor System. Oxford Univ. Press; New York: 1992. pp. 427–433.
-
- Becker W, King WM, Fuchs AF, Jürgens R, Johanson G, Kornhuber HH. Accuracy of goal-directed saccades and mechanisms of error correction. In: Fuchs AF, Becker W, editors. Progress in Oculomotor Research. Elsevier; New York: 1981. pp. 29–37.
-
- Bergeron A, Guitton D. Fixation neurons in the superior colliculus encode distance between current and desired gaze positions. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:932–939. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron A, Guitton D. In multiple-step gaze shifts: omnipause (OPNs) and collicular fixation neurons encode gaze position error; OPNs gate saccades. J Neurophysiol. 2002;88:1726–1742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

