In vivo roles for matrix metalloproteinase-9 in mature hippocampal synaptic physiology and plasticity
- PMID: 17493927
- PMCID: PMC4415272
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00202.2007
In vivo roles for matrix metalloproteinase-9 in mature hippocampal synaptic physiology and plasticity
Abstract
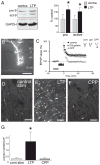
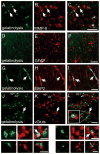
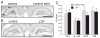
Extracellular proteolysis is an important regulatory nexus for coordinating synaptic functional and structural plasticity, but the identity of such proteases is incompletely understood. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) have well-known, mostly deleterious roles in remodeling after injury or stroke, but their role in nonpathological synaptic plasticity and function in intact adult brains has not been extensively investigated. Here we address the role of MMP-9 in hippocampal synaptic plasticity using both gain- and loss-of-function approaches in urethane-anesthetized adult rats. Acute blockade of MMP-9 proteolytic activity with inhibitors or neutralizing antibodies impairs maintenance, but not induction, of long-term potentiation (LTP) at synapses formed between Schaffer-collaterals and area CA1 dendrites. LTP is associated with significant increases in levels of MMP-9 and proteolytic activity within the potentiated neuropil. By introducing a novel application of gelatin-substrate zymography in vivo, we find that LTP is associated with significantly elevated numbers of gelatinolytic puncta in the potentiated neuropil that codistribute with immunolabeling for MMP-9 and for markers of synapses and dendrites. Such increases in proteolytic activity require NMDA receptor activation. Exposing intact area CA1 neurons to recombinant-active MMP-9 induces a slow synaptic potentiation that mutually occludes, and is occluded by, tetanically evoked potentiation. Taken together, our data reveal novel roles for MMP-mediated proteolysis in regulating nonpathological synaptic function and plasticity in mature hippocampus.
Figures


References
-
- Antonova I, Arancio O, Trillat AC, Wang HG, Zablow L, Udo H, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD. Rapid increase in clusters of presynaptic proteins at onset of long-lasting potentiation. Science. 2001;294:1547–1550. - PubMed
-
- Arai K, Lee SR, Lo EH. Essential role for ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase in matrix metalloproteinase-9 regulation in rat cortical astrocytes. Glia. 2003;43:254–264. - PubMed
-
- Baranes D, Lederfein D, Huang YY, Chen M, Bailey CH, Kandel ER. Tissue plasminogen activator contributes to the late phase of LTP and to synaptic growth in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway. Neuron. 1998;21:813–825. - PubMed
-
- Barlow JZ, Kelley KA, Bozdagi O, Huntley GW. Testing the role of the cell-surface molecule Thy-1 in regeneration and plasticity of connectivity in the CNS. Neuroscience. 2002;111:837–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

