Alarm symptoms in early diagnosis of cancer in primary care: cohort study using General Practice Research Database
- PMID: 17493982
- PMCID: PMC1871798
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39171.637106.AE
Alarm symptoms in early diagnosis of cancer in primary care: cohort study using General Practice Research Database
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the association between alarm symptoms and the subsequent diagnosis of cancer in a large population based study in primary care.
Design: Cohort study.
Setting: UK General Practice Research Database. Patients 762 325 patients aged 15 years and older, registered with 128 general practices between 1994 and 2000. First occurrences of haematuria, haemoptysis, dysphagia, and rectal bleeding were identified in patients with no previous cancer diagnosis.
Main outcome measure: Positive predictive value of first occurrence of haematuria, haemoptysis, dysphagia, or rectal bleeding for diagnoses of neoplasms of the urinary tract, respiratory tract, oesophagus, or colon and rectum during three years after symptom onset. Likelihood ratio and sensitivity were also estimated.
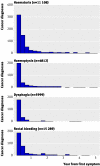
Results: 11.108 first occurrences of haematuria were associated with 472 new diagnoses of urinary tract cancers in men and 162 in women, giving overall three year positive predictive values of 7.4% (95% confidence interval 6.8% to 8.1%) in men and 3.4% (2.9% to 4.0%) in women. After 4812 new episodes of haemoptysis, 220 diagnoses of respiratory tract cancer were made in men (positive predictive value 7.5%, 6.6% to 8.5%) and 81 in women (4.3%, 3.4% to 5.3%). After 5999 new diagnoses of dysphagia, 150 diagnoses of oesophageal cancer were made in men (positive predictive value 5.7%, 4.9% to 6.7%) and 81 in women (2.4%, 1.9 to 3.0%). After 15 289 episodes of rectal bleeding, 184 diagnoses of colorectal cancer were made in men (positive predictive value 2.4%, 2.1% to 2.8%) and 154 in women (2.0%, 1.7% to 2.3%). Predictive values increased with age and were strikingly high, for example, in men with haemoptysis aged 75-84 (17.1%, 13.5% to 21.1%) and in men with dysphagia aged 65-74 (9.0%, 6.8% to 11.7%).
Conclusion: New onset of alarm symptoms is associated with an increased likelihood of a diagnosis of cancer, especially in men and in people aged over 65. These data provide support for the early evaluation of alarm symptoms in an attempt to identify underlying cancers at an earlier and more amenable stage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Alarm symptoms in primary care.BMJ. 2007 May 19;334(7602):1013-4. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39212.467037.BE. BMJ. 2007. PMID: 17510105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Donnell CA. Variation in GP referral rates: what can we learn from the literature? Fam Pract 2000;17:462-71. - PubMed
-
- Department of Health. Referral guidelines for suspected cancer London: DH, 2000.
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Referral guidelines for suspected cancer London: NICE, 2005
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources