Biomarkers of obesity and subsequent cardiovascular events
- PMID: 17494057
- PMCID: PMC4682894
- DOI: 10.1093/epirev/mxm005
Biomarkers of obesity and subsequent cardiovascular events
Abstract
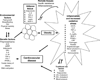
Obesity is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, but the mechanisms for increased cardiovascular risk in obesity are still unclear. Inflammation and increased oxidative stress are two potential mechanisms proposed to play a major role in the morbidity associated with obesity. Studies that investigate these mechanisms rely on biomarkers, but validated biomarkers for obesity-related cardiovascular outcomes are lacking. By finding optimal biomarkers, diagnostic criteria for cardiovascular diseases can be refined in the obese beyond "traditional" risk factors to identify early pathologic processes. The objective of this review is to identify potential early biomarkers resulting from obesity and associated with cardiovascular disease. Studies were initially identified through the search engine PubMed by using the keywords "obesity" and "biomarker." Subsequently, combinations of the keywords "obesity," "biomarker," "cardiovascular risk," "adipose tissue," "adipokine," "adipocytokine," and "oxidative stress" were used. The SOURCE database and Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) were used to obtain more information on the biomarkers. Results of the searches yielded a large number of potential biomarkers that occur in obesity and which either correlate with traditional cardiovascular risk factors or predict subsequent cardiovascular events. Several biomarkers are promising regarding their biologic properties, but they require further validation in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory biomarkers for predicting cardiovascular disease.Clin Biochem. 2013 Oct;46(15):1353-71. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.05.070. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Clin Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23756129 Review.
-
MicroRNAs as early biomarkers in obesity and related metabolic and cardiovascular diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(32):5704-17. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990364. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448489 Review.
-
Obesity and cardiovascular disease: role of adipose tissue, inflammation, and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2013 Sep;15(2):49-57. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2013-0025. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2013. PMID: 25436732 Review.
-
Roles of adiponectin and oxidative stress in obesity-associated metabolic and cardiovascular diseases.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2014 Mar;15(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s11154-013-9271-7. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2014. PMID: 24026768 Review.
-
Roles of oxidative stress, adiponectin, and nuclear hormone receptors in obesity-associated insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2014 Aug;19(2):75-88. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2014-0001. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2014. PMID: 25390017 Review.
Cited by
-
A Pilot Study for Metabolic Profiling of Obesity-Associated Microbial Gut Dysbiosis in Male Wistar Rats.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 18;11(2):303. doi: 10.3390/biom11020303. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33670496 Free PMC article.
-
Pericardial fat volume correlates with inflammatory markers: the Framingham Heart Study.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010 May;18(5):1039-45. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.343. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010. PMID: 19875999 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity Biomarkers: Exploring Factors, Ramification, Machine Learning, and AI-Unveiling Insights in Health Research.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jun 22;6(7):e70169. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70169. eCollection 2025 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40551726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating levels of adiponectin, leptin, fetuin-A and retinol-binding protein in patients with tuberculosis: markers of metabolism and inflammation.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038703. Epub 2012 Jun 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22685600 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between obesity and changes in adult BMI over time and colon cancer risk.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008 May;16(5):1099-104. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.42. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008. PMID: 18356841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA. 2006;295:1549–1555. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Graubard BI, Williamson DF, et al. Excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. JAMA. 2005;293:1861–1867. - PubMed
-
- Fontaine KR, Redden DT, Wang C, et al. Years of life lost due to obesity. JAMA. 2003;289:187–193. - PubMed
-
- Goodman E, Dolan LM, Morrison JA, et al. Factor analysis of clustered cardiovascular risks in adolescence: obesity is the predominant correlate of risk among youth. Circulation. 2005;111:1970–1977. - PubMed
-
- Fung TT, Rimm EB, Spiegelman D, et al. Association between dietary patterns and plasma biomarkers of obesity and cardiovascular disease risk. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;73:61–67. - PubMed

