Induction of MxA gene expression by influenza A virus requires type I or type III interferon signaling
- PMID: 17494065
- PMCID: PMC1933351
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00546-06
Induction of MxA gene expression by influenza A virus requires type I or type III interferon signaling
Abstract
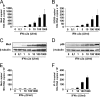
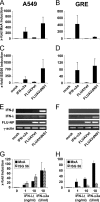
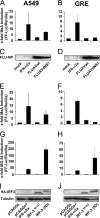
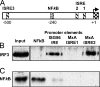
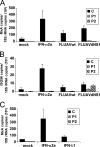
The human MxA gene belongs to the class of interferon (IFN)-stimulated genes (ISGs) involved in antiviral resistance against influenza viruses. Here, we studied the requirements for MxA induction by influenza A virus infection. MxA is transcriptionally upregulated by type I (alpha and beta) and type III (lambda) IFNs. Therefore, MxA is widely used in gene expression studies as a reliable marker for IFN bioactivity. It is not known, however, whether viruses can directly activate MxA expression in the absence of secreted IFN. By using an NS1-deficient influenza A virus and human cells with defects in IFN production or the STAT1 gene, we studied the induction profile of MxA by real-time reverse transcriptase PCR. The NS1-deficient virus is known to be a strong activator of the IFN system because NS1 acts as a viral IFN-antagonistic protein. Nevertheless, MxA gene expression was not inducible by this virus upon infection of IFN nonproducer cells and STAT1-null cells. Likewise, neither IFN-alpha nor IFN-lambda had a sizeable effect on the STAT1-null cells, indicating that MxA expression requires STAT1 signaling and cannot be triggered directly by virus infection. In contrast, the expression of the IFN-stimulated gene ISG56 was induced by influenza virus in these cells, confirming that ISG56 differs from MxA in being directly inducible by viral triggers in an IFN-independent way. In summary, our study reveals that MxA is a unique marker for the detection of type I and type III IFN activity during virus infections and IFN therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Alexopoulou, L., A. C. Holt, R. Medzhitov, and R. A. Flavell. 2001. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413:732-738. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli, G., E. Simeoni, O. Turriziani, R. Tesoro, A. Redaelli, L. Roffi, L. Antonelli, M. Pistello, and F. Dianzani. 1999. Correlation of interferon-induced expression of MxA mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells with the response of patients with chronic active hepatitis C to IFN-α therapy. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 19:243-251. - PubMed
-
- Asahina, Y., N. Izumi, M. Uchihara, O. Noguchi, Y. Nishimura, K. Inoue, K. Ueda, K. Tsuchiya, K. Hamano, J. Itakura, and S. Miyake. 2003. Interferon-stimulated gene expression and hepatitis C viral dynamics during different interferon regimens. J. Hepatol. 39:421-427. - PubMed
-
- Baechler, E. C., F. M. Batliwalla, G. Karypis, P. M. Gaffney, W. A. Ortmann, K. J. Espe, K. B. Shark, W. J. Grande, K. M. Hughes, V. Kapur, P. K. Gregersen, and T. W. Behrens. 2003. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:2610-2615. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

