Poliovirus induces Bax-dependent cell death mediated by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
- PMID: 17494073
- PMCID: PMC1933371
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02690-06
Poliovirus induces Bax-dependent cell death mediated by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
Abstract
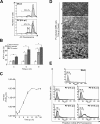
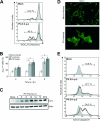
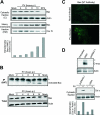
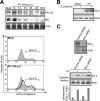
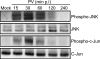
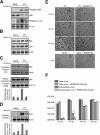
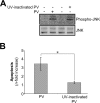
Poliovirus (PV) is the causal agent of paralytic poliomyelitis, a disease that involves the destruction of motor neurons associated with PV replication. In PV-infected mice, motor neurons die through an apoptotic process. However, mechanisms by which PV induces cell death in neuronal cells remain unclear. Here, we demonstrate that PV infection of neuronal IMR5 cells induces cytochrome c release from mitochondria and loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential, both of which are evidence of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. PV infection also activates Bax, a proapoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family; this activation involves its conformational change and its redistribution from the cytosol to mitochondria. Neutralization of Bax by vMIA protein expression prevents cytochrome c release, consistent with a contribution of PV-induced Bax activation to mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Interestingly, we also found that c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) is activated soon after PV infection and that the PV-cell receptor interaction alone is sufficient to induce JNK activation. Moreover, the pharmacological inhibition of JNK by SP600125 inhibits Bax activation and cytochrome c release. This is, to our knowledge, the first demonstration of JNK-mediated Bax-dependent apoptosis in PV-infected cells. Our findings contribute to our understanding of poliomyelitis pathogenesis at the cellular level.
Figures
References
-
- Ammendolia, M. G., A. Tinari, A. Calcabrini, and F. Superti. 1999. Poliovirus infection induces apoptosis in CaCo-2 cells. J. Med. Virol. 59:122-129. - PubMed
-
- Ammendrup, A., A. Maillard, K. Nielsen, N. Aabenhus Andersen, P. Serup, O. Dragsbaek Madsen, T. Mandrup-Poulsen, and C. Bonny. 2000. The c-Jun amino-terminal kinase pathway is preferentially activated by interleukin-1 and controls apoptosis in differentiating pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 49:1468-1476. - PubMed
-
- Aoki, H., P. M. Kang, J. Hampe, K. Yoshimura, T. Noma, M. Matsuzaki, and S. Izumo. 2002. Direct activation of mitochondrial apoptosis machinery by c-Jun N-terminal kinase in adult cardiac myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 277:10244-10250. - PubMed
-
- Arnoult, D., L. M. Bartle, A. Skaletskaya, D. Poncet, N. Zamzami, P. U. Park, J. Sharpe, R. J. Youle, and V. S. Goldmacher. 2004. Cytomegalovirus cell death suppressor vMIA blocks Bax- but not Bak-mediated apoptosis by binding and sequestering Bax at mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:7988-7993. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

