X-box-binding protein 1 activates lytic Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in combination with protein kinase D
- PMID: 17494074
- PMCID: PMC1933364
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00154-07
X-box-binding protein 1 activates lytic Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in combination with protein kinase D
Abstract
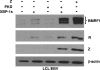
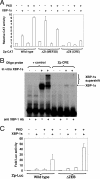
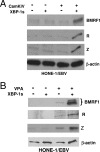
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) establishes a latent form of infection in memory B cells, while antibody-secreting plasma cells often harbor the lytic form of infection. The switch between latent and lytic EBV infection is mediated by the two viral immediate-early proteins BZLF1 (Z) and BRLF1 (R), which are not expressed in latently infected B cells. Here we demonstrate that a cellular transcription factor that plays an essential role in plasma cell differentiation, X-box-binding protein 1 (XBP-1), also activates the transcription of the two EBV immediate-early gene promoters. In reporter gene assays, XBP-1 alone was sufficient to activate the R promoter, whereas the combination of XBP-1 and protein kinase D (PKD) was required for efficient activation of the Z promoter. Most importantly, the expression of XBP-1 and activated PKD was sufficient to induce lytic viral gene expression in EBV-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and lymphoblastoid cells, while an XBP-1 small interfering RNA inhibited constitutive lytic EBV gene expression in lymphoblastoid cells. These results suggest that the plasma cell differentiation factor XBP-1, in combination with activated PKD, can mediate the reactivation of EBV, thereby allowing the viral life cycle to be intimately linked to plasma cell differentiation.
Figures


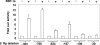
References
-
- Back, S. H., K. Lee, E. Vink, and R. J. Kaufman. 2006. Cytoplasmic IRE1alpha-mediated XBP1 mRNA splicing in the absence of nuclear processing and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 281:18691-18706. - PubMed
-
- Baron, C. L., and V. Malhotra. 2002. Role of diacylglycerol in PKD recruitment to the TGN and protein transport to the plasma membrane. Science 295:325-328. - PubMed
-
- Bhende, P. M., W. T. Seaman, H. J. Delecluse, and S. C. Kenney. 2004. The EBV lytic switch protein, Z, preferentially binds to and activates the methylated viral genome. Nat. Genet. 36:1099-1104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

