Accuracy of pre- and postcontrast 3D time-of-flight MR angiography in patients with acute ischemic stroke: correlation with catheter angiography
- PMID: 17494671
- PMCID: PMC8134328
Accuracy of pre- and postcontrast 3D time-of-flight MR angiography in patients with acute ischemic stroke: correlation with catheter angiography
Abstract
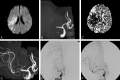
Background and purpose: 3D time-of-flight (TOF) MR angiography (MRA) is insensitive to slow flow; however, the use of MR imaging contrast agents helps to visualize slow-flow vessels and avoids overestimation of vascular occlusion. The purpose of this study was to correlate pre- and postcontrast 3D TOF MRA with the results of conventional angiography during endovascular reperfusion therapy and to determine the accuracy of postcontrast 3D TOF MRA.
Materials and methods: Thirteen patients who underwent endovascular reperfusion therapy for acute ischemic stroke were retrospectively analyzed. MR imaging techniques included single-slab 3D TOF MRA with and without contrast, as well as perfusion-weighted imaging. Angiography during reperfusion therapy was used as a standard of reference. Affected arteries were divided into segments either proximal or distal to the lesion, and pre- and postcontrast MRA signals were graded as absent, diminished or narrowed, or normal.
Results: In 2 of 5 patients with arterial stenosis and 6 of 8 patients with complete occlusion, MRA signal intensity proximal to each lesion was absent, indicating a proximal pseudo-occlusion on precontrast MRA. Postcontrast MRA demonstrated an arterial signal intensity proximal to the stenotic or occlusive lesions in all 13 patients. Arterial signal intensity distal to the occlusion was identified on postcontrast MRA in 7 of 8 patients having complete occlusion, and the extent of occlusion on postcontrast MRA was similar to results of conventional angiography.
Conclusion: In this small series, postcontrast 3D TOF MRA more accurately delineated the extent of stenotic or occlusive arterial lesions than precontrast MRA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of pre- and postcontrast 3D time-of-flight MR angiography for the evaluation of distal intracranial branch occlusions in acute ischemic stroke.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002 Apr;23(4):557-67. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002. PMID: 11950644 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution postcontrast time-of-flight MR angiography of intracranial perforators at 7.0 Tesla.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 16;10(3):e0121051. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121051. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25774881 Free PMC article.
-
Follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated by flow diverter: comparison of three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography (3D-TOF-MRA) and contrast-enhanced MR angiography (CE-MRA) sequences with digital subtraction angiography as the gold standard.J Neurointerv Surg. 2016 Jan;8(1):81-6. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011449. Epub 2014 Oct 28. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016. PMID: 25352582
-
Contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the intracranial circulation.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2003 Nov;11(4):599-614. doi: 10.1016/s1064-9689(03)00064-3. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2003. PMID: 15018113 Review.
-
[Diagnosis of renal artery stenosis with magnetic resonance angiography and stenosis quantification].J Mal Vasc. 2000 Dec;25(5):312-320. J Mal Vasc. 2000. PMID: 11148391 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Mismatch between TOF MR Angiography and CT Angiography of the Middle Cerebral Artery may be a Critical Sign in Cerebrovascular Dynamics.Yonsei Med J. 2018 Jan;59(1):80-84. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.80. Yonsei Med J. 2018. PMID: 29214780 Free PMC article.
-
MR angiography in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: adequate to evaluate vasospasm-induced vascular narrowing?Neurosurg Rev. 2010 Oct;33(4):431-9. doi: 10.1007/s10143-010-0267-4. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Neurosurg Rev. 2010. PMID: 20532584
-
Imaging in childhood arterial ischaemic stroke.Neuroradiology. 2010 Jun;52(6):577-89. doi: 10.1007/s00234-010-0704-7. Epub 2010 May 6. Neuroradiology. 2010. PMID: 20445969 Review.
-
MRI for collateral assessment pre-thrombectomy and association with outcome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neuroradiology. 2023 Jun;65(6):1001-1014. doi: 10.1007/s00234-023-03127-8. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Neuroradiology. 2023. PMID: 36847834 Free PMC article.
-
The morphology of the human cerebrovascular system.Hum Brain Mapp. 2018 Dec;39(12):4962-4975. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24337. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018. PMID: 30265762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Korogi Y, Takahashi M, Mabuchi N, et al. Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusion: diagnostic accuracy of three-dimensional, Fourier transform, time-of-flight MR angiography. Radiology 1994;193:187–93 - PubMed
-
- Axel L. Blood flow effects in magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Annu 1986;237–44 - PubMed
-
- Yano T, Kodama T, Suzuki Y, et al. Gadolinium-enhanced 3D time-of-flight MR angiography: experimental and clinical evaluation. Acta Radiol 1997;38:47–54 - PubMed
-
- Pedraza S, Silva Y, Mendez J, et al. Comparison of preperfusion and postperfusion magnetic resonance angiography in acute stroke. Stroke 2004;35:2105–10 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
