Cerebral aneurysmal arteriopathy in an adult patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
- PMID: 17494674
- PMCID: PMC8134320
Cerebral aneurysmal arteriopathy in an adult patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
Abstract
In adult patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), cerebral arteritis usually takes the form of arterial wall thickening, stenosis, and occlusion, leading to cerebral ischemia and infarction. Aneurysms and intracranial hemorrhage are much less commonly associated with cerebral vasculitis. For reasons not entirely clear, this form is seen more often in pediatric patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. We report an adult patient with cerebral aneurysmal arteriopathy who presented shortly after his AIDS-defining illness in a setting of severe immune suppression and high viral load.
Figures
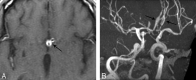
References
-
- Nogueras C, Sala M, Sasal M, et al. Recurrent stroke as a manifestation of primary angiitis of the central nervous system in a patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Arch Neurol 2002;59:468–73 - PubMed
-
- Brannagan TH. Retroviral-associated vasculitis of the nervous system. Neurol Clin 1997;15:927–44 - PubMed
-
- Bagasra O, Lavi E, Bobroski L, et al. Cellular reservoirs of HIV-1 in the central nervous system of infected individuals: identification by the combination of in situ polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. AIDS 1996;10:573–85 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
