Multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat assay analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains
- PMID: 17494714
- PMCID: PMC1932968
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02451-06
Multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat assay analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains
Abstract
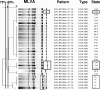
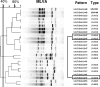
Our objective was to determine if a multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat assay (MLVA) for Staphylococcus aureus could predict pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) types (i.e., USA types), thus allowing us to replace PFGE with a simpler and more rapid typing method. One hundred three well-characterized isolates representing 13 major lineages of S. aureus were tested by both PFGE and MLVA. MLVA was performed using a rapid DNA extraction technique and PCR primers for sdrCDE, clfA, clfB, sspA, and spa. PFGE was performed with genomic DNA fragments generated using SmaI, as per CDC protocols. Banding patterns were analyzed both visually and with BioNumerics software. All isolates were typeable with MLVA and PFGE. MLVA patterns were highly reproducible. PFGE separated the isolates into 13 types with 42 subtypes. Using any band difference to designate a novel MLVA type, MLVA produced 45 types, including 9 clusters containing multiple isolates. Using BioNumerics and a cutoff of >75% relatedness, MLVA produced 28 types, 11 of which contained >1 isolate. Epidemiologically related outbreak isolates of USA300-0114 from five states clustered in one MLVA pattern. USA100 isolates were present in several unrelated (<40%) MLVA types. A cutoff of >80% separated outbreak strains of USA300-0114 into three distinct MLVA types. MLVA did not differentiate community methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) lineages (USA300, USA400, USA1000, and USA1100) from health care MRSA lineages (USA100, USA200, or USA500). The ability of MLVA to differentiate among strains that are indistinguishable by PFGE may be of epidemiologic value and warrants further study.
Figures

References
-
- Deresinski, S. 2005. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an evolutionary, epidemiologic, and therapeutic odyssey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 40:562-573. - PubMed
-
- Francois, P., A. Huyghe, Y. Charbonnier, M. Bento, S. Herzig, I. Topolski, B. Fleury, D. Lew, P. Vaudaux, S. Harbarth, W. van Leeuwen, A. van Belkum, D. S. Blanc, D. Pittet, and J. Schrenzel. 2005. Use of an automated multiple-locus, variable-number tandem repeat-based method for rapid and high-throughput genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43:3346-3355. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fridkin, S. K., C. D. Steward, J. R. Edwards, E. R. Pryor, J. E. McGowan, Jr., L. K. Archibald, R. P. Gaynes, F. C. Tenover, and Project Intensive Care Antimicrobial Resistance Epidemiology (ICARE) Hospitals. 1999. Surveillance of antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in United States hospitals: Project ICARE phase 2. Clin. Infect. Dis. 29:245-252. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert, F. B., A. Fromageau, L. Gelineau, and B. Poutrel. 2006. Differentiation of bovine Staphylococcus aureus isolates by use of polymorphic tandem repeat typing. Vet. Microbiol. 117:297-303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

