Plant domestication, a unique opportunity to identify the genetic basis of adaptation
- PMID: 17494757
- PMCID: PMC1876441
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700643104
Plant domestication, a unique opportunity to identify the genetic basis of adaptation
Abstract
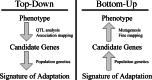
Despite the fundamental role of plant domestication in human history and the critical importance of a relatively small number of crop plants to modern societies, we still know little about adaptation under domestication. Here we focus on efforts to identify the genes responsible for adaptation to domestication. We start from a historical perspective, arguing that Darwin's conceptualization of domestication and unconscious selection provides valuable insight into the evolutionary history of crops and also provides a framework to evaluate modern methods used to decipher the genetic mechanisms underlying phenotypic change. We then review these methods, framing the discussion in terms of the phenotype-genotype hierarchy. Top-down approaches, such as quantitative trait locus and linkage disequilibrium mapping, start with a phenotype of interest and use genetic analysis to identify candidate genes. Bottom-up approaches, alternatively, use population genetic analyses to identify potentially adaptive genes and then rely on standard bioinformatics and reverse genetic tools to connect selected genes to a phenotype. We discuss the successes, advantages, and challenges of each, but we conclude that bottom-up approaches to understanding domestication as an adaptive process hold greater promise both for the study of adaptation and as a means to identify genes that contribute to agronomically important traits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Harter AV, Gardner KA, Falush D, Lentz DL, Bye RA, Rieseberg LH. Nature. 2004;430:201–205. - PubMed
-
- Heun M, SchaferPregl R, Klawan D, Castagna R, Accerbi M, Borghi B, Salamini F. Science. 1997;278:1312–1314.
-
- Darwin CR. The Foundations of the Origin of Species: Two Essays Written in 1842 and 1844. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ Press; 1909.
-
- Darwin CR. The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication. London: Murray; 1868.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

