ApoER2/VLDL receptor and Dab1 in the rostral migratory stream function in postnatal neuronal migration independently of Reelin
- PMID: 17494763
- PMCID: PMC1895980
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611391104
ApoER2/VLDL receptor and Dab1 in the rostral migratory stream function in postnatal neuronal migration independently of Reelin
Abstract
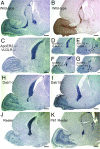
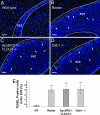
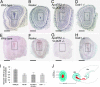
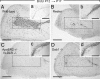
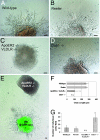
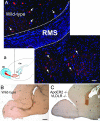
Postnatal migration of interneuron precursors from the subventricular zone to the olfactory bulb occurs in chains that form the substrate for the rostral migratory stream. Reelin is suggested to induce detachment of neuroblasts from the chains when they arrive at the olfactory bulb. Here we show that ApoER2 and possibly very-low-density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) and their intracellular adapter protein Dab1 are involved in chain formation most likely independent of Reelin. F-spondin, which is present in the stream, may act as ligand for ApoER2 and VLDLR. In mice lacking either both receptors or Dab1 chain formation is severely compromised, and as a consequence the rostral migratory stream is virtually absent and neuroblasts accumulate in the subventricular zone. The mutant animals exhibit severe neuroanatomical defects in the subventricular zone and in the olfactory bulb. These data demonstrate a cell-autonomous function of ApoER2, and most likely VLDLR and Dab1, in postnatal migration of neuroblasts in the forebrain, which is suggested to depend on ligands other than Reelin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

