Single-molecule mass spectrometry in solution using a solitary nanopore
- PMID: 17494764
- PMCID: PMC1866312
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611085104
Single-molecule mass spectrometry in solution using a solitary nanopore
Abstract
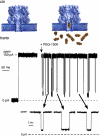
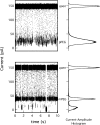
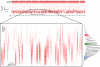
We introduce a two-dimensional method for mass spectrometry in solution that is based on the interaction between a nanometer-scale pore and analytes. As an example, poly(ethylene glycol) molecules that enter a single alpha-hemolysin pore cause distinct mass-dependent conductance states with characteristic mean residence times. The conductance-based mass spectrum clearly resolves the repeat unit of ethylene glycol, and the mean residence time increases monotonically with the poly(ethylene glycol) mass. This technique could prove useful for the real-time characterization of molecules in solution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Coulter WH. US Patent. 2,656,508. 1953.
-
- Ito T, Sun L, Crooks RM. Anal Chem. 2003;75:2399–2406. - PubMed
-
- Saleh OA, Sohn LL. Nano Lett. 2003;3:37–38.
-
- Heins EA, Siwy ZS, Baker LA, Martin CR. Nano Lett. 2005;5:1824–1829. - PubMed
-
- Song LZ, Hobaugh MR, Shustak C, Cheley S, Bayley H, Gouaux JE. Science. 1996;274:1859–1866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

