Diverse Kir modulators act in close proximity to residues implicated in phosphoinositide binding
- PMID: 17495041
- PMCID: PMC2075264
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.133157
Diverse Kir modulators act in close proximity to residues implicated in phosphoinositide binding
Abstract
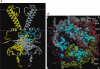
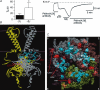
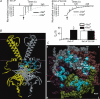
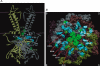
Inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) channels were the first shown to be directly activated by phosphoinositides in general and phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP(2)) in particular. Atomic resolution structures have been determined for several mammalian and bacterial Kir channels. Basic residues, identified through mutagenesis studies to contribute to the sensitivity of the channel to PIP(2), have been mapped onto the three dimensional channel structure and their localization has given rise to a plausible model that can explain channel activation by PIP(2). Moreover, mapping onto the three-dimensional channel structure sites involved in the modulation of Kir channel activity by a diverse group of regulatory molecules, revealed a striking proximity to residues implicated in phosphoinositide binding. These observations support the hypothesis that the observed dependence of diverse modulators on channel-PIP(2) interactions stems from their localization within distances that can affect PIP(2)-interacting residues.
Figures

References
-
- Abraham MR, Jahangir A, Alekseev AE, Terzic A. Channelopathies of inwardly rectifying potassium channels. FASEB J. 1999;13:1901–1910. - PubMed
-
- Baukrowitz T, Schulte U, Oliver D, Herlitze S, Krauter T, Tucker SJ, et al. PIP2 and PIP as determinants for ATP inhibition of KATP channels. Science. 1998;282:1141–1144. - PubMed
-
- Bichet D, Haass FA, Jan LY. Merging functional studies with structures of inward-rectifier K+ channels. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:957–967. - PubMed
-
- Breitwieser GE, Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and β-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985;317:538–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

