Prenatal stress in the rat results in increased blood pressure responsiveness to stress and enhanced arterial reactivity to neuropeptide Y in adulthood
- PMID: 17495046
- PMCID: PMC2075315
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.130252
Prenatal stress in the rat results in increased blood pressure responsiveness to stress and enhanced arterial reactivity to neuropeptide Y in adulthood
Abstract
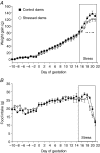
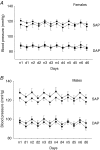
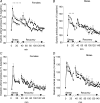
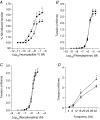
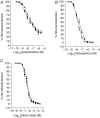
We have shown previously that stress in the pregnant rat leads to a heightened cardiovascular response to restraint in adult offspring. The present study was undertaken to explore further the persistent cardiovascular effects of prenatal stress, with a focus on peripheral vascular function. Sprague-Dawley female rats were exposed to restraint/bright light three times daily in the last week of pregnancy. Litters from stressed and control females were cross-fostered to control dams to eliminate possible effects of maternal stress on nursing behaviour. At 120 days, offspring cardiovascular variables were measured by radiotelemetry. Reactivity of mesenteric small arteries was assessed by myography, and responses to electrical field stimulation determined. Resting cardiovascular parameters in prenatally stressed (PS) offspring were similar to controls but PS rats showed a greater increase in systolic blood pressure following restraint stress (P<0.05). Recovery was also prolonged in PS animals compared with controls and was of longer duration in PS females than in PS males (P<0.05). Adult PS females, but not males, also had elevated basal plasma corticosterone levels in comparison with controls (P<0.05). Vascular reactivity to neuropeptide Y (P<0.05) and electrical field stimulation (P<0.05) in mesenteric arteries was also significantly increased in PS animals. Vascular responses to adrenergic agonists as well as endothelial dilator function did not differ between PS and controls. We conclude that prenatal stress during late gestation has long-lasting effects on cardiovascular responsiveness and vascular reactivity to neuropeptide Y in the offspring.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prenatal stress alters cardiovascular responses in adult rats.J Physiol. 2004 May 15;557(Pt 1):273-85. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.056911. Epub 2004 Mar 19. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15034122 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal social stress in the rat programmes neuroendocrine and behavioural responses to stress in the adult offspring: sex-specific effects.J Neuroendocrinol. 2010 Apr;22(4):258-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2010.01969.x. Epub 2010 Jan 27. J Neuroendocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20136688
-
Vulnerability versus resilience to prenatal stress in male and female rats; implications from gene expression profiles in the hippocampus and frontal cortex.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013 Oct;23(10):1226-46. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.09.011. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23199416
-
Sex-specific differences in the mechanisms for enhanced thromboxane A2-mediated vasoconstriction in adult offspring exposed to prenatal hypoxia.Biol Sex Differ. 2024 Jun 19;15(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00627-x. Biol Sex Differ. 2024. PMID: 38898532 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of maternal stress on the sexual behavior of male offspring.Monogr Neural Sci. 1983;9:169-75. doi: 10.1159/000406889. Monogr Neural Sci. 1983. PMID: 6350861 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The effects of progressive muscular relaxation and breathing control technique on blood pressure during pregnancy.Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2016 May-Jun;21(3):331-6. doi: 10.4103/1735-9066.180382. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2016. PMID: 27186213 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of low level maternal Pb exposure and prenatal stress on offspring stress challenge responsivity.Neurotoxicology. 2008 Nov;29(6):928-39. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2008.09.010. Epub 2008 Oct 5. Neurotoxicology. 2008. PMID: 18951918 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in major depression and comorbidity of cardiometabolic disorders: impact of prenatal stress and immune exposures.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Jan;44(1):59-70. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0146-1. Epub 2018 Jul 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30030541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ingenuity pathway analysis of clozapine-induced obesity.Obes Facts. 2008;1(2):93-102. doi: 10.1159/000127278. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Obes Facts. 2008. PMID: 20054168 Free PMC article.
-
The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis: Development, Programming Actions of Hormones, and Maternal-Fetal Interactions.Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 Jan 13;14:601939. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.601939. eCollection 2020. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33519393 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander BT, Hendon AE, Ferril G, Dwyer TM. Renal denervation abolishes hypertension in low-birth-weight offspring from pregnant rats with reduced uterine perfusion. Hypertension. 2005;45:754–758. - PubMed
-
- Bertram CE, Hanson MA. Animal models and programming of the metabolic syndrome. Br Med Bull. 2001;60:103–121. - PubMed
-
- Butz GM, Davisson RL. Long-term telemetric measurement of cardiovascular parameters in awake mice: a physiological genomics tool. Physiol Genomics. 2001;5:89–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

