Identification of regions critically affecting kinetics and allosteric regulation of the Escherichia coli ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase by modeling and pentapeptide-scanning mutagenesis
- PMID: 17496097
- PMCID: PMC1951854
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00481-07
Identification of regions critically affecting kinetics and allosteric regulation of the Escherichia coli ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase by modeling and pentapeptide-scanning mutagenesis
Abstract
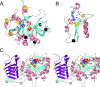
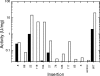
ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (ADP-Glc PPase) is the enzyme responsible for the regulation of bacterial glycogen synthesis. To perform a structure-function relationship study of the Escherichia coli ADP-Glc PPase enzyme, we studied the effects of pentapeptide insertions at different positions in the enzyme and analyzed the results with a homology model. We randomly inserted 15 bp in a plasmid with the ADP-Glc PPase gene. We obtained 140 modified plasmids with single insertions of which 21 were in the coding region of the enzyme. Fourteen of them generated insertions of five amino acids, whereas the other seven created a stop codon and produced truncations. Correlation of ADP-Glc PPase activity to these modifications validated the enzyme model. Six of the insertions and one truncation produced enzymes with sufficient activity for the E. coli cells to synthesize glycogen and stain in the presence of iodine vapor. These were in regions away from the substrate site, whereas the mutants that did not stain had alterations in critical areas of the protein. The enzyme with a pentapeptide insertion between Leu(102) and Pro(103) was catalytically competent but insensitive to activation. We postulate this region as critical for the allosteric regulation of the enzyme, participating in the communication between the catalytic and regulatory domains.
Figures


References
-
- Ballicora, M. A., J. R. Dubay, C. H. Devillers, and J. Preiss. 2005. Resurrecting the ancestral enzymatic role of a modulatory subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 280:10189-10195. - PubMed
-
- Ballicora, M. A., A. A. Iglesias, and J. Preiss. 2004. ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase: a regulatory enzyme for plant starch synthesis. Photosynth. Res. 79:1-24. - PubMed
-
- Ballicora, M. A., J. I. Sesma, A. A. Iglesias, and J. Preiss. 2002. Characterization of chimeric ADPglucose pyrophosphorylases of Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Importance of the C-terminus on the selectivity for allosteric regulators. Biochemistry 41:9431-9437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

