Expression by streptomyces lividans of the rat alpha integrin CD11b A-domain as a secreted and soluble recombinant protein
- PMID: 17497024
- PMCID: PMC1791067
- DOI: 10.1155/2007/54327
Expression by streptomyces lividans of the rat alpha integrin CD11b A-domain as a secreted and soluble recombinant protein
Abstract
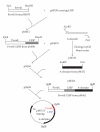
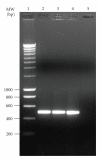
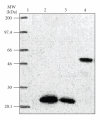
We already reported the use of a long synthetic signal peptide (LSSP) to secrete the Streptomyces sp. TO1 amylase by Streptomyces lividans strain. We herein report the expression and secretion of the rat CD11b A-domain using the same LSSP and S. lividans as host strain. We have used the Escherichia coli/Streptomyces shuttle vector pIJ699 for the cloning of the A-domain DNA sequence downstream of LSSP and under the control of the constitutive ermE-up promoter of Streptomyces erythraeus. Using this construct and S. lividans as a host strain, we achieved the expression of 8 mg/L of soluble secreted recombinant form of the A-domain of the rat leukocyte beta2 integrin CD11/CD18 alpha M subunit (CD11b). This secreted recombinant CD11b A-domain reacted with a function blocking antibody showing that this protein is properly folded and probably functional. These data support the capability of Streptomyces to produce heterologous recombinant proteins as soluble secreted form using the "LSSP" synthetic signal peptide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recombinant production of Streptococcus equisimilis streptokinase by Streptomyces lividans.Microb Cell Fact. 2007 Jul 5;6:20. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-6-20. Microb Cell Fact. 2007. PMID: 17610745 Free PMC article.
-
Functional large-scale production of a novel Jonesia sp. xyloglucanase by heterologous secretion from Streptomyces lividans.J Biotechnol. 2006 Feb 24;121(4):498-507. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.08.002. Epub 2005 Sep 15. J Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16168511
-
Cloning of the rat CR3 alphaM (CD11b) subunit, expression and binding assay of recombinant isolated CD11b VA (A-domain) and ICAM-1 Ig modules.Arch Inst Pasteur Tunis. 2002;79(1-4):11-7. Arch Inst Pasteur Tunis. 2002. PMID: 15072240
-
Heterologous biopharmaceutical protein expression in Streptomyces.Trends Biotechnol. 1997 Aug;15(8):315-20. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7799(97)01062-7. Trends Biotechnol. 1997. PMID: 9263479 Review.
-
The Cellular Mechanisms that Ensure an Efficient Secretion in Streptomyces.Antibiotics (Basel). 2018 Apr 14;7(2):33. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics7020033. Antibiotics (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29661993 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New approaches to achieve high level enzyme production in Streptomyces lividans.Microb Cell Fact. 2016 Feb 4;15:28. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0425-7. Microb Cell Fact. 2016. PMID: 26846788 Free PMC article.
-
Streptomycetes: Attractive Hosts for Recombinant Protein Production.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 20;11:1958. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01958. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32973711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic and evolutionary insights into the closely-related species Streptomyces coelicolor and Streptomyces lividans deduced from high-resolution comparative genomic hybridization.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 1;11:682. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-682. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21122120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Williams ST, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Wellington EM, Sneath PH, Sackin MJ. Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. Journal of General Microbiology. 1983;129(6):1743–1813. - PubMed
-
- Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA. Practical Streptomyces Genetics. Norwich, UK: John Innes Foundation; 2000.
-
- Binnie C, Cossar JD, Stewart DIH. Heterologous biopharmaceutical protein expression in Streptomyces . Trends in Biotechnology. 1997;15(8):315–320. - PubMed
-
- Hong B, Li Y, Van Mellaert G, Anné J. Expression of biologically active human tumor necrosis factor β by Streptomyces lividans . Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2003;30(3):209–214. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

