Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 6 in human periapical lesions
- PMID: 17497030
- PMCID: PMC1804300
- DOI: 10.1155/2007/38210
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 6 in human periapical lesions
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate the presence of the cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in human periapical lesions.
Subjects and methods: Samples were obtained from three groups of teeth: symptomatic teeth, asymptomatic lesions, and uninflamed periradicular tissues as a control.
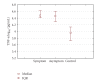
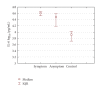
Results: TNF-alpha levels were significantly increased in symptomatic lesions compared to control. Group with asymptomatic lesions had significantly higher concentrations compared to control. There were no significant differences in TNF-alpha levels between symptomatic and asymptomatic lesions. In group with symptomatic lesions, IL-6 levels were significantly higher than in group with asymptomatic lesions. The IL-6 levels in symptomatic group also showed significantly higher concentration in comparison with control group. In asymptomatic group, the IL-6 level had significantly higher concentrations compared to control.
Conclusion: These results indicate that symptomatic lesions represent an immunologically active stage of disease, and asymptomatic lesions are the point from which the process advances toward healing.
Figures
References
-
- Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquort JR. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: W. B. Saunders; 1995.
-
- Chen C-P, Hertzberg M, Jiang Y, Graves DT. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor receptor signaling is not required for bacteria-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone loss but is essential for protecting the host from a mixed anaerobic infection. American Journal of Pathology. 1999;155(6):2145–2152. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yamano S, Atkinson JC, Baum BJ, Fox PC. Salivary gland cytokine expression in NOD and normal BALB/c mice. Clinical Immunology. 1999;92(3):265–275. - PubMed
-
- Radics T, Kiss C, Tar I, Márton IJ. Interleukin-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in apical periodontitis: correlation with clinical and histologic findings of the involved teeth. Oral Microbiology and Immunology. 2003;18(1):9–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

