German evidence-based guidelines for the treatment of Psoriasis vulgaris (short version)
- PMID: 17497162
- PMCID: PMC1910890
- DOI: 10.1007/s00403-007-0744-y
German evidence-based guidelines for the treatment of Psoriasis vulgaris (short version)
Abstract
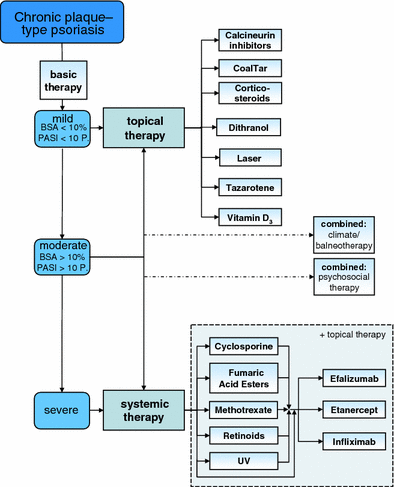
Psoriasis vulgaris is a common and chronic inflammatory skin disease which has the potential to significantly reduce the quality of life in severely affected patients. The incidence of psoriasis in Western industrialized countries ranges from 1.5 to 2%. Despite the large variety of treatment options available, patient surveys have revealed insufficient satisfaction with the efficacy of available treatments and a high rate of medication non-compliance. To optimize the treatment of psoriasis in Germany, the Deutsche Dermatologische Gesellschaft and the Berufsverband Deutscher Dermatologen (BVDD) have initiated a project to develop evidence-based guidelines for the management of psoriasis. The guidelines focus on induction therapy in cases of mild, moderate, and severe plaque-type psoriasis in adults. The short version of the guidelines reported here consist of a series of therapeutic recommendations that are based on a systematic literature search and subsequent discussion with experts in the field; they have been approved by a team of dermatology experts. In addition to the therapeutic recommendations provided in this short version, the full version of the guidelines includes information on contraindications, adverse events, drug interactions, practicality, and costs as well as detailed information on how best to apply the treatments described (for full version, please see Nast et al., JDDG, Suppl 2:S1-S126, 2006; or http://www.psoriasis-leitlinie.de ).
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10495380', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10495380/'}]}
- Richards HL, Fortune DG, O’Sullivan TM, Main CJ, Griffiths CE (1999) Patients with psoriasis and their compliance with medication. J Am Acad Dermatol 41(4):581–583 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1046/j.1365-2133.1996.d01-1035.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.1996.d01-1035.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8915141', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8915141/'}]}
- Nevitt GJ, Hutchinson PE (1996) Psoriasis in the community: prevalence, severity and patients’ beliefs and attitudes towards the disease. Br J Dermatol 135(4):533–537 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/s00105-005-0906-9', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/s00105-005-0906-9'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15711815', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15711815/'}]}
- Schmid-Ott G, Malewski P, Kreiselmaier I, Mrowietz U (2005) Psychosoziale Folgen der Psoriasis—eine empirische Studie über die Krankheitslast bei 3753 Betroffenen. Hautarzt 56(5):466–472 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0190-9622(99)70112-X', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0190-9622(99)70112-x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10459113', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10459113/'}]}
- Rapp SR, Feldman SR, Exum ML, Fleischer AB Jr, Reboussin DM (1999) Psoriasis causes as much disability as other major medical diseases. J Am Acad Dermatol 41(3 Pt 1): 401–407 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1046/j.1087-0024.2003.09102.x', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1087-0024.2003.09102.x'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15083780', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15083780/'}]}
- Stern RS, Nijsten T, Feldman SR, Margolis DJ, Rolstad T (2004) Psoriasis is common, carries a substantial burden even when not extensive, and is associated with widespread treatment dissatisfaction. J Invest Dermatol Symp Proc 9(2):136–139 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical