HIF-1alpha induced-VEGF overexpression in bone marrow stem cells protects cardiomyocytes against ischemia
- PMID: 17498737
- PMCID: PMC1995444
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.04.001
HIF-1alpha induced-VEGF overexpression in bone marrow stem cells protects cardiomyocytes against ischemia
Abstract
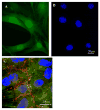
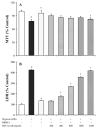
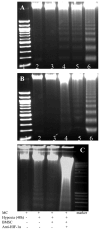
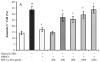
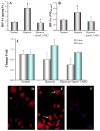
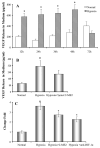
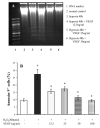
Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) is a proangiogenic transcription factor stabilized and activated under hypoxia. It regulates the expression of numerous target genes, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and other cytoprotective proteins. In this study, we hypothesized that bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs) secrete growth factors which protect cardiomyocytes via HIF-1alpha pathway. BMSCs were obtained from transgenic mice overexpressing green fluorescent protein (GFP). The study was carried out in vitro using co-culture of BMSCs with cardiomyocytes. LDH release, MTT uptake, DNA fragmentation and annexin-V positive cells were used as cell injury markers. The level of HIF-1alpha protein as well as its activated form and VEGF were measured by ELISA. The expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in BMSCs was analyzed by quantitative PCR and cellular localization was determined by immunohistochemistry. LDH release was increased and MTT uptake was decreased after exposure of cardiomyocytes to hypoxia for 30 h, which were prevented by co-culturing cardiomyocytes with BMSCs. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by hypoxia and H(2)O(2) was also reduced by co-culture with BMSCs. VEGF release from BMSCs was significantly increased in parallel with high level of HIF-1alpha in BMSCs following anoxia or hypoxia in a time-dependent manner. Although no significant up-regulation could be seen in HIF-1alpha mRNA, HIF-1alpha protein and its activated form were markedly increased and translocated to the nucleus or peri-nuclear area. The increase and translocation of HIF-1alpha in BMSCs were completely blocked by 2-methoxyestradiol (2-ME2; 5 mumol), a HIF-1alpha inhibitor. Moreover, the protection of cardiomyocytes by BMSC and VEGF secretion was abolished by neutralizing HIF-1alpha antibody in a concentration dependent manner (200-3200 ng/ml). Bone marrow stem cells protect cardiomyocytes by up-regulation of VEGF via activating HIF-1alpha.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest
Figures

References
-
- Xue T, Cho HC, Akar FG, Tsang SY, Jones SP, Marban E, et al. Functional integration of electrically active cardiac derivatives from genetically engineered human embryonic stem cells with quiescent recipient ventricular cardiomyocytes: insights into the development of cell-based pacemakers. Circulation. 2005 Jan 4;111(1):11–20. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Haider H, Ahmad N, Zhang D, Ashraf M. Evidence for ischemia induced host-derived bone marrow cell mobilization into cardiac allografts. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006 Sep;41(3):478–87. - PubMed
-
- Uemura R, Xu M, Ahmad N, Ashraf M. Bone marrow stem cells prevent left ventricular remodeling of ischemic heart through paracrine signaling. Circ Res. 2006 Jun 9;98(11):1414–21. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda K, Fujita J. Mesenchymal, but not hematopoietic, stem cells can be mobilized and differentiate into cardiomyocytes after myocardial infarction in mice. Kidney Int. 2005 Nov;68(5):1940–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 HL 074272/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 083236/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 087246/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL081859/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080686/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 081859/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL074272/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL023597/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 080686/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 70062/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070062/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083236/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087246/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

