Cloning and large-scale expansion of epitope-specific equine cytotoxic T lymphocytes using an anti-equine CD3 monoclonal antibody and human recombinant IL-2
- PMID: 17498813
- PMCID: PMC2002571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2007.04.001
Cloning and large-scale expansion of epitope-specific equine cytotoxic T lymphocytes using an anti-equine CD3 monoclonal antibody and human recombinant IL-2
Abstract
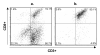
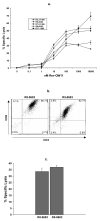
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes are involved in controlling intracellular pathogens in many species, including horses. Particularly, CTL are critical for the control of equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV), a lentivirus that infects horses world-wide. In humans and animal models, CTL clones are valuable for evaluating the fine specificity of epitope recognition, and for adoptive immunotherapy against infectious and neoplastic diseases. Cloned CTL would be equally useful for similar studies in the horse. Here we present the first analysis of a method to generate equine CTL clones. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were obtained from an EIAV-infected horse and stimulated with the EIAV Rev-QW11 peptide. Sorted CD8+ T cells were cloned by limiting dilution, and expanded without further antigen addition using irradiated PBMC, anti-equine CD3, and human recombinant IL-2. Clones could be frozen and thawed without detrimental effects, and could be subsequently expanded to numbers exceeding 2 x 10(9)cells. Flow cytometry of expanded clones confirmed the CD3+/CD8+ phenotype, and chromium release assays confirmed CTL activity. Finally, sequencing TCR beta chain genes confirmed clonality. Our results provide a reliable means to generate large numbers of epitope-specific equine CTL clones that are suitable for use in downstream applications, including functional assays and adoptive transfer studies.
Figures


References
-
- Breathnach CC, Soboll G, Suresh M, Lunn DP. Equine herpesvirus-1 infection induces IFN-gamma production by equine T lymphocyte subsets. Vet.Immunol.Immunopathol. 2005;103:207–215. - PubMed
-
- Paillot R, Daly JM, Juillard V, Minke JM, Hannant D, Kydd JH. Equine interferon gamma synthesis in lymphocytes after in vivo infection and in vitro stimulation with EHV-1. Vaccine. 2005;23:4541–4551. - PubMed
-
- Paillot R, Ellis SA, Daly JM, Audonnet JC, Minke JM, Davis-Poynter N, Hannant D, Kydd JH. Characterisation of CTL and IFN-gamma synthesis in ponies following vaccination with a NYVAC-based construct coding for EHV-1 immediate early gene, followed by challenge infection. Vaccine. 2006;24:1490–1500. - PubMed
-
- Paillot R, Daly JM, Luce R, Montesso F, Davis-Poynter N, Hannant D, Kydd JH. Frequency and phenotype of EHV-1 specific, IFN-gamma synthesising lymphocytes in ponies: the effects of age, pregnancy and infection. Dev.Comp Immunol. 2007;31:202–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

