GABA(A) receptors: structure and function in the basal ganglia
- PMID: 17499107
- PMCID: PMC2648504
- DOI: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)60003-4
GABA(A) receptors: structure and function in the basal ganglia
Abstract
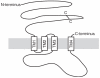
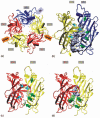
gamma-Aminobutyric acid type A (GABA(A)) receptors, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors responsible for fast inhibition in the basal ganglia, belong to the superfamily of "cys-cys loop" ligand-gated ion channels. GABA(A) receptors form as pentameric assemblies of subunits, with a central Cl(-) permeable pore. On binding of two GABA molecules to the extracellular receptor domain, a conformational change is induced in the oligomer and Cl(-), in most adult neurons, moves into the cell leading to an inhibitory hyperpolarization. Nineteen mammalian subunit genes have been identified, each showing distinct regional and cell-type-specific expression. The combinatorial assembly of the subunits generates considerable functional diversity. Here we place the focus on GABA(A) receptor expression in the basal ganglia: striatum, globus pallidus, substantia nigra and subthalamic nucleus, where, in addition to the standard alpha1beta2/3gamma2 receptor subtype, significant levels of other subunits (alpha2, alpha3, alpha4, gamma1, gamma3 and delta) are expressed in some nuclei.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distribution of the major gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptor subunits in the basal ganglia and associated limbic brain areas of the adult rat.J Comp Neurol. 2001 May 14;433(4):526-49. doi: 10.1002/cne.1158. J Comp Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11304716
-
An electron microscope immunocytochemical study of GABA(B) R2 receptors in the monkey basal ganglia: a comparative analysis with GABA(B) R1 receptor distribution.J Comp Neurol. 2004 Aug 9;476(1):65-79. doi: 10.1002/cne.20210. J Comp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15236467
-
GABA(B) receptors: structure and function.Prog Brain Res. 2007;160:43-57. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)60004-6. Prog Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17499108 Review.
-
Expression of 10 GABA(A) receptor subunit messenger RNAs in the motor-related thalamic nuclei and basal ganglia of Macaca mulatta studied with in situ hybridization histochemistry.Neuroscience. 1998 Jul;85(1):179-204. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00634-9. Neuroscience. 1998. PMID: 9607711
-
The diversity of GABA(A) receptor subunit distribution in the normal and Huntington's disease human brain.Adv Pharmacol. 2015;73:223-64. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2014.11.010. Epub 2015 Jan 17. Adv Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25637443 Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleus accumbens GABAergic inhibition generates intense eating and fear that resists environmental retuning and needs no local dopamine.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Jun;37(11):1789-802. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12194. Epub 2013 Mar 31. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23551138 Free PMC article.
-
Desire and dread from the nucleus accumbens: cortical glutamate and subcortical GABA differentially generate motivation and hedonic impact in the rat.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 18;5(6):e11223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011223. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20585461 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding bee cleptoparasitism through comparative transcriptomics of Coelioxoides waltheriae and its host Tetrapedia diversipes.Sci Rep. 2024 May 29;14(1):12361. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56261-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38811580 Free PMC article.
-
Ion channels in dry eye disease.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023 Apr;71(4):1215-1226. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_3020_22. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37026252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between GABRG2 and Self-Rating of the Effects of Alcohol in a French Young Adult Sample.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025 Jan 24;18:291-304. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S483830. eCollection 2025. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025. PMID: 39882063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumann SW, Baur R, Sigel E. Forced subunit assembly in alpha1beta2gamma2 GABAA receptors. Insight into the absolute arrangement. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:46020–46025. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

