Differences in binding of (99m)Tc-disintegrins to integrin alphavbeta3 on tumor and vascular cells
- PMID: 17499726
- PMCID: PMC1986642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.02.004
Differences in binding of (99m)Tc-disintegrins to integrin alphavbeta3 on tumor and vascular cells
Abstract
Disintegrins, which contain an Arg-Gly-Asp sequence in their binding domains are antagonists of integrins such as alphavbeta3. The purpose of this study was to compare a range of disintegrins with different integrin selectivities for their binding behavior in vitro to vascular endothelial cells bearing alphavbeta3 and to cultured tumor cells which express alphavbeta3.
Methods: Five disintegrins (bitistatin, kistrin, flavoridin, VLO4 and echistatin) and a cyclic pentapeptide, c[RGDyK], were radiolabeled with (99m)Tc and tested for binding to cells in vitro.
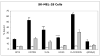
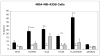
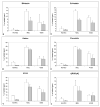
Results: (99m)Tc-Kistrin, flavoridin and VLO4 had the highest binding, (99m)Tc-echistatin had moderate binding, and (99m)Tc-bitistatin and (99m)Tc-c[RGDyK] had low binding to cells. The observed binding was attributed to alphavbeta3 to various extents: echistatin, bitistatin>kistrin>flavoridin>VLO4. Cancer cells internalized bound disintegrins after binding, but endothelial cells did not. After binding to endothelial cells, (99m)Tc-kistrin was not displaced by competing peptide or plasma proteins.
Conclusions: These data suggest that radiolabeled kistrin, flavoridin and VLO4 may have advantages over labeled bitistatin and small cyclic peptides for targeting alphavbeta3 in vivo. Since receptor-bound radioligand is not internalized by endothelial cells, disintegrins may provide an advantage for targeting alphavbeta3 on vasculature because they bind strongly to surface receptors and are not readily displaced.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Disintegrin interaction with alpha V beta 3 integrin on human umbilical vein endothelial cells: expression of ligand-induced binding site on beta 3 subunit.Exp Cell Res. 1996 May 25;225(1):132-42. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0164. Exp Cell Res. 1996. PMID: 8635506
-
[99mTc]HYNIC-RGD for imaging integrin alphavbeta3 expression.Nucl Med Biol. 2006 Nov;33(8):945-52. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2006.09.001. Nucl Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 17127166
-
Comparison of iodine-123-disintegrins for imaging thrombi and emboli in a canine model.J Nucl Med. 1996 Mar;37(3):476-82. J Nucl Med. 1996. PMID: 8772651
-
99mTc-Regioselectively addressable functionalized template-[cyclo-(Arg-Gly-Asp-d-Phe-Lys)]4.2008 Feb 9 [updated 2008 May 8]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Feb 9 [updated 2008 May 8]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641939 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
99mTc(CO)3-Pyrazolyl-cyclo(Arg-Gly-Asp-D-Tyr-Lys).2007 Jul 9 [updated 2007 Aug 27]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2007 Jul 9 [updated 2007 Aug 27]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641243 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Encoding of Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents for Tumor Imaging.ACS Synth Biol. 2020 Feb 21;9(2):392-401. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.9b00416. Epub 2020 Jan 22. ACS Synth Biol. 2020. PMID: 31922737 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Value of 99mTc-3PRGD2 SPECT/CT in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma with Negative 131I Whole-Body Scan and Elevated Thyroglobulin Level.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 11;8(1):473. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-19036-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29323252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Felding-Habermann B, Cheresh DA. Vitronectin and its receptors. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 1993;5:864–868. - PubMed
-
- Suehiro K, Smith JW, Plow EF. The ligand recognition specificity of β3 integrins. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:10365–10371. - PubMed
-
- Shattil SJ. Function and regulation of the β3 integrins in hemostasis and vascular biology. Thromb Haemost. 1995;74:149–155. - PubMed
-
- Brooks PC, Cheresh DA, Clark AF. Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994;264:569–571. - PubMed
-
- Cox D, Aoki T, Seki J, Motoyama Y, Yoshida K. The pharmacology of the integrins. Medicinal Research Reviews. 1994;14:195–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

