The novel ER membrane protein PRO41 is essential for sexual development in the filamentous fungus Sordaria macrospora
- PMID: 17501918
- PMCID: PMC3694341
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05694.x
The novel ER membrane protein PRO41 is essential for sexual development in the filamentous fungus Sordaria macrospora
Abstract
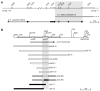
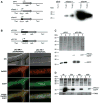
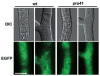
The filamentous fungus Sordaria macrospora develops complex fruiting bodies (perithecia) to propagate its sexual spores. Here, we present an analysis of the sterile mutant pro41 that is unable to produce mature fruiting bodies. The mutant carries a deletion of 4 kb and is complemented by the pro41 open reading frame that is contained within the region deleted in the mutant. In silico analyses predict PRO41 to be an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane protein, and a PRO41-EGFP fusion protein colocalizes with ER-targeted DsRED. Furthermore, Western blot analysis shows that the PRO41-EGFP fusion protein is present in the membrane fraction. A fusion of the predicted N-terminal signal sequence of PRO41 with EGFP is secreted out of the cell, indicating that the signal sequence is functional. pro41 transcript levels are upregulated during sexual development. This increase in transcript levels was not observed in the sterile mutant pro1 that lacks a transcription factor gene. Moreover, microarray analysis of gene expression in the mutants pro1, pro41 and the pro1/41 double mutant showed that pro41 is partly epistatic to pro1. Taken together, these data show that PRO41 is a novel ER membrane protein essential for fruiting body formation in filamentous fungi.
Figures



Comment in
-
How to build a fungal fruit body: from uniform cells to specialized tissue.Mol Microbiol. 2007 May;64(4):873-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05711.x. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17501912
References
-
- Beers J, Glerum DM, Tzagoloff A. Purification, characterization, and localization of yeast Cox17p, a mitochondrial copper shuttle. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:33191–33196. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol. 2004;340:783–795. - PubMed
-
- Berteaux-Lecellier V, Picard M, Thompson-Coffe C, Zickler D, Panvier-Adoutte A, Simonet JM. A nonmammalian homolog of the PAF1 gene (Zellweger syndrome) discovered as a gene involved in caryogamy in the fungus Podospora anserina. Cell. 1995;81:1043–1051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

