Virtual histology
- PMID: 17502324
- PMCID: PMC1994391
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2007.116384
Virtual histology
Abstract
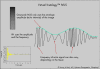
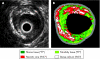
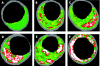
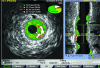
As a luminogram, coronary angiography provides a good overview of the coronary artery tree. Using quantitative coronary measurements, the degree of coronary obstruction can be determined. The limitation of coronary angiography is that it does not provide information on the arterial wall structure and therefore cannot assess the extent of atherosclerosis. Knowledge about adaptive coronary remodelling processes as compensatory enlargement of the coronary artery has focused diagnostic interest on the non-stenotic lesions of the coronary tree. Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) can reveal discrepancies between the extent of coronary atherosclerosis and angiography imaging by in vivo plaque imaging. Spectrum analysis of IVUS-derived radiofrequency (RF) data enables a more detailed analysis of plaque composition and morphology. Preliminary in vitro studies correlated four histological plaque components with a specific spectrum analysis of the RF data. The different components (fibrous, fibrofatty, necrotic core and dense calcium) are colour coded. Coronary tissue maps were reconstructed from RF data using IVUS-Virtual Histology (VH IVUS) software (Real-Time VH, Volcano Corporation, Rancho Cordova, California, USA). VH IVUS has the potential to detect high-risk lesions and can provide new insights into the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease. VH IVUS allows the differentiation of different lesion types based on information derived from histopathology. The in vivo specific histological analysis of coronary atherosclerosis may allow better stratification of treatment of patients with coronary artery disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
[Intravascular ultrasound for recognition of atherosclerotic plaques and plaque composition. Current state of the diagnostic value].Herz. 2011 Aug;36(5):402-9. doi: 10.1007/s00059-011-3485-9. Herz. 2011. PMID: 21732096 Review. German.
-
Assessment of early atherosclerosis in de novo heart transplant recipients: analysis with intravascular ultrasound-derived radiofrequency analysis.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2008 Jan;27(1):26-30. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2007.10.005. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2008. PMID: 18187083
-
Prospective validation of standardized, 3-dimensional, quantitative coronary computed tomographic plaque measurements using radiofrequency backscatter intravascular ultrasound as reference standard in intermediate coronary arterial lesions: results from the ATLANTA (assessment of tissue characteristics, lesion morphology, and hemodynamics by angiography with fractional flow reserve, intravascular ultrasound and virtual histology, and noninvasive computed tomography in atherosclerotic plaques) I study.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011 Feb;4(2):198-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2010.10.008. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011. PMID: 21349459
-
Head-to-head comparison of coronary plaque evaluation between multislice computed tomography and intravascular ultrasound radiofrequency data analysis.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2008 Apr;1(2):176-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2008.01.007. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2008. PMID: 19463297
-
[Intravascular ultrasound investigation with virtual hystology in the study of coronary artery lesions].Kardiologiia. 2009;49(12):58-61. Kardiologiia. 2009. PMID: 20038284 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Computational Model of Drug-Coated Balloon Delivery in a Patient-Specific Arterial Vessel with Heterogeneous Tissue Composition.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2016 Dec;7(4):406-419. doi: 10.1007/s13239-016-0273-y. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2016. PMID: 27443840 Free PMC article.
-
An inverse method for mechanical characterization of heterogeneous diseased arteries using intravascular imaging.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 18;11(1):22540. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01874-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34795350 Free PMC article.
-
[Intravascular ultrasound for recognition of atherosclerotic plaques and plaque composition. Current state of the diagnostic value].Herz. 2011 Aug;36(5):402-9. doi: 10.1007/s00059-011-3485-9. Herz. 2011. PMID: 21732096 Review. German.
-
Consensus of the National Heart Center in collaboration With the Saudi Arabian Cardiac Interventional Society on the Clinical Use of Intracoronary Imaging.J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2024 Sep 1;36(2):137-157. doi: 10.37616/2212-5043.1387. eCollection 2024. J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39469526 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of diagnosing unstable plaque in patients with acute coronary syndrome using iMap-IVUS.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015 Nov;16(11):924-30. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1500206. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015. PMID: 26537210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nissen S E, Yock P. Intravascular ultrasound: Novel pathophysiological insights and current clinical applications. Circulation 2001103604–616. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials