Efficacy of a novel rifamycin derivative, ABI-0043, against Staphylococcus aureus in an experimental model of foreign-body infection
- PMID: 17502404
- PMCID: PMC1913231
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00120-07
Efficacy of a novel rifamycin derivative, ABI-0043, against Staphylococcus aureus in an experimental model of foreign-body infection
Abstract
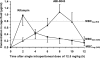
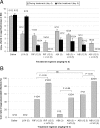
We compared the efficacy of a novel rifamycin derivative, ABI-0043, with that of rifampin, alone and in combination with levofloxacin, against methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 in a guinea pig tissue-cage infection model. The MIC, logarithmic-growth-phase minimal bactericidal concentration, and stationary-growth-phase minimal bactericidal concentration of ABI-0043 were 0.001, 0.008, and 0.25 microg/ml, respectively; the corresponding concentrations of rifampin were 0.016, 0.8, and 3.6 microg/ml, respectively. After a single intraperitoneal dose of 12.5 mg/kg of body weight, the peak concentration in cage fluid was 1.13 micarog/ml of ABI-0043 and 0.98 microg/ml of rifampin. Five days after completion of treatment, levofloxacin administered alone (5 mg/kg/12 h) resulted in bacterial counts in cage fluid that were similar to those for untreated controls (>8.0 log(10) CFU/ml), whereas rifampin and ABI-0043 administered alone (12.5 mg/kg/12 h) decreased the mean titers of bacteria +/- standard deviations to 1.43 +/- 0.28 log(10) and 1.57 +/- 0.53 log(10) CFU/ml, respectively, in cage fluid. In combination with levofloxacin, both rifamycins cleared bacteria from the cage fluid. The cure rates of cage-associated infections with rifampin and ABI-0043 administered alone were 46% and 58%, respectively, and increased to 88% and 92% in combination with levofloxacin. Emergence of rifamycin resistance was observed in 42% of cages after ABI-0043 therapy and in 38% of cages after rifampin therapy; no emergence of resistance occurred with combination treatment with levofloxacin. In conclusion, ABI-0043 had cure rates comparable to that of rifampin. ABI-0043 in combination with a quinolone has the potential for treatment of implant-associated infections caused by susceptible strains of S. aureus, potentially without drug-drug interactions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Linezolid alone or combined with rifampin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in experimental foreign-body infection.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Mar;53(3):1142-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00775-08. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19075065 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of high doses of levofloxacin in experimental foreign-body infection by methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Dec;50(12):4011-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00523-06. Epub 2006 Oct 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 17015630 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of dalbavancin, alone and in combination with rifampicin, against meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a foreign-body infection model.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013 Sep;42(3):220-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.05.019. Epub 2013 Jul 20. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013. PMID: 23880168
-
[Rifampicin in the treatment of staphylococcal infection].Antibiot Med Biotekhnol. 1986 Aug;31(8):568-74. Antibiot Med Biotekhnol. 1986. PMID: 3532936 Review. Russian. No abstract available.
-
Development potential of rifalazil and other benzoxazinorifamycins.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006 Jun;15(6):603-23. doi: 10.1517/13543784.15.6.603. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16732714 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and treatment of implant-associated septic arthritis and osteomyelitis.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2008 Sep;10(5):394-403. doi: 10.1007/s11908-008-0064-1. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2008. PMID: 18687204
-
Linezolid alone or combined with rifampin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in experimental foreign-body infection.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Mar;53(3):1142-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00775-08. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19075065 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic effect of rifampin on the efficacy of high-dose levofloxacin in staphylococcal experimental foreign-body infection.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Oct;52(10):3681-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00458-08. Epub 2008 Aug 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18676888 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug-resistant organisms in military wounds from Iraq and Afghanistan.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008 Jun;466(6):1356-62. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0212-9. Epub 2008 Mar 18. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008. PMID: 18347888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gentamicin improves the activities of daptomycin and vancomycin against Enterococcus faecalis in vitro and in an experimental foreign-body infection model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Oct;55(10):4821-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00141-11. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21807979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brandt, C. M., W. W. Sistrunk, M. C. Duffy, A. D. Hanssen, J. M. Steckelberg, D. M. Ilstrup, and D. R. Osmon. 1997. Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infection treated with debridement and prosthesis retention. Clin. Infect. Dis. 24914-919. - PubMed
-
- Brause, B. D. 2005. Infections with prostheses in bones and joints, p. 1332-1337. In G. L. Mandell, J. E. Bennett, and R. Dolin (ed.), Principles and practice of infectious diseases. W.B. Saunders, Washington, DC.
-
- Costerton, J. W., P. S. Stewart, and E. P. Greenberg. 1999. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 2841318-1322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

